Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and scrambled it to make a type specimen book. It has survived not only five centuries, but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry. Lorem Ipsum has been the industry's standard dummy text ever since the 1500s, when an unknown printer took a galley of type and but also the leap into electronic typesetting, remaining essentially unchanged. It was popularised in the 1960s with the release of Letraset sheets containing Lorem Ipsum passages, and more recently with desktop publishing software like Aldus PageMaker including versions of Lorem Ipsum.

For Canadians holding an Overseas Citizen of India (OCI) card who want to invest in Indian real estate without physically travelling to India, the question is common:👉 Can you buy property through a Power of Attorney (POA)?👉 What is the exact lawful process?👉 What are the required documents, legal risks, and government rules?This guide answers these questions in simple language — but with professional legal precision — so you and your family can make informed, compliant investment decisions in Indian property law.Can an OCI Card Holder Buy Property in India Without Coming to India?Yes — Generally, YesAs per Indian law under the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) and its Rules (especially Foreign Exchange Management (Non-Debt Instruments) Rules, 2019), an OCI card holder is legally allowed to:✅ Purchase residential & commercial property in India❌ Except agricultural land, plantation property, or farmhouses (unless inherited) Under FEMA Section 5 & Section 46, OCIs enjoy general permission to acquire immovable property without prior approval of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), provided all payments are made through permissible banking channels. 📌 Important Legal Foundation📜 1. FEMA 1999 & Non-Debt Instruments RulesContains the core rules on foreign acquisition and transfer of immovable property.OCIs fall under the permitted class (similar to Non-Resident Indians (NRIs)).Purchase of residential or commercial property requires no RBI approval; agricultural-related property does. 📜 2. Transfer of Property Act, 1882Governs how property rights can be transferred through sale deeds, wills, or POA.Under Section 5 & Section 54 (Definitions) it recognises valid conveyance through registered instruments. 📜 3. Indian Registration Act, 1908All instruments dealing with immovable property (including sale deeds and POA) must be registered at the local Sub-Registrar’s office for legal effect.Notarised but unregistered POA is legally ineffective as a transfer instrument. Can a POA Be Used to Buy Property Without Physical Presence?Yes — But Only If Done Correctly.A Power of Attorney allows your appointed representative in India to act on your behalf for specific property dealings including:➡ Identifying property➡ Negotiating price➡ Signing the sale agreement➡ Executing the sale deed➡ Attending registration formalitiesBut there are legal requirements:1️⃣ Special/Specific Power of Attorney (SPA)a. Must be carefully drafted to clearly list powers — e.g., negotiation, signing agreements, registration, tax payments.b. A general POA is insufficient for property purchase. 2️⃣ Attestation/ApostilleIf executed outside India, the POA must be:a. Notarised in Canada (or local state)b. Then either:✔ Apostilled (if Canada is Hague member), or✔ Attested by the Indian Consulate/EmbassyThis ensures Indian authorities accept it as authentic. 3️⃣ Registration in IndiaThe POA must be:📍 Registered with the Sub-Registrar Office where the property is located📍 Paid applicable stamp duty (state-specific)Note: A notarised POA alone — without registration — is not legally effective to deal with property. 🧭 Step-by-Step Process to Buy Property via POA (Canadian OCI)This process helps you purchase legally and securely without traveling:🔎 Step 1: Identify the Propertya. Confirm seller’s titleb. Conduct title and encumbrance searchc. Ensure no litigation or fraud history‼ This is where legal due diligence done by an expert law firm like KHA Advocates protects you.🖋️ Step 2: Draft and Execute Power of AttorneyYour Canadian OCI must:✔ Choose the attorney (trustworthy person in India)✔ Draft a specific SPA✔ Notarise it in Canada (state)✔ Apostille/Consulate attestation✔ Ship properly sealed to India✔ Get it registered locally with stamp duty paid📌 POA must be time-bound, specific & covers registration authority.💸 Step 3: Arrange FEMA-Compliant PaymentPayment for property must follow FEMA guidelines:✅ Through inward remittanceOR✅ From your NRE, NRO, or FCNR(B) account❌ Cash/Foreign currency notes/Traveler’s cheques NOT ALLOWED. 📄 Step 4: Sale Agreement & RegistrationYour attorney will:1. Sign the Agreement to Sell2. Pay earnest deposit3. Prepare the Sale Deed4. Pay stamp duty & registration fees5. Register the sale deed at Sub-Registrar’s OfficeOnly a registered Sale Deed transfers ownership. — POA itself does not transfer rights legally. 🧾 Step 5: PAN & Tax ComplianceOCI must hold:✔ Indian PAN Card (Income Tax purpose)✔ Comply with TDS requirements (if applicable)✔ File Income Tax return if rental income earnedPAN is essential for registration and taxation. 🏦 Step 6: Repatriation of Sale Proceeds (Future)If the OCI sells later and wants to bring money abroad:✔ Repatriation of sale proceeds is allowed subject to RBI rules and compliance with FEMA and tax laws.📌 Common Legal Pitfalls to Avoid❌ Using a Notarised POA only without registration❌ Ambiguous or blank powers❌ POA not consulate-attested or apostilled❌ Missing PAN or TDS compliance❌ Paying outside permissible channelsYes — a Canadian OCI card holder can legally buy residential or commercial property in India without coming to the country, provided all legal formalities are followed, especially through a registered Power of Attorney and FEMA-compliant payment methods.This method is entirely lawful and widely used, but depends heavily on:✔ Properly drafted, attested & registered POA✔ Clear title & due diligence✔ RBI/FEMA compliance✔ Local Registration complianceWhy Choose KHA Advocates?We specialize in:✔ OCI & NRI Property Transactions✔ Power of Attorney Drafting & Registration✔ FEMA & RBI Compliance✔ Property Title Verification✔ Sale Deed Registration Support✔ Cross-Border Real Estate AdvisoryWe assist clients globally — including Canada, USA, UK, Australia & Middle East.Contact Details :KHA Advocates [Law Firm]Google Location : https://share.google/oFGKBu7PpPPNJalp0 New Town, Hatiara, Dhankal, Noapara, Kolkata, West Bengal 700157📞 Phone: +91-94-777-5-888-5📱 WhatsApp: +91-8010-555-666📧 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in🌐 Website: https://www.khaadvocates.com 🗓 Book Consultation: 👉 https://khaadvocates.com/book-consultation
Read More
Buying or selling a property is one of the biggest financial transactions of life. Yet, many people rush into it without proper legal guidance—only to face disputes, fraud, or loss later. The sale agreement and the sale deed are the backbone of any property transaction. Any mistake in these documents can cost you money, peace of mind, or even the property itself.That’s where a property lawyer plays a critical role. In this blog, we explain why you need a property lawyer for drafting and verifying your sale agreement and sale deed, the risks of not having one, relevant case laws, and how our law firm can help you.Why Are Sale Agreement and Sale Deed So Important?Sale Agreement: This is the preliminary contract that records the terms and conditions agreed upon between the buyer and the seller—price, payment schedule, possession date, default clauses, etc. It sets the foundation for the final sale deed.Sale Deed: This is the final registered document that transfers ownership of the property from the seller to the buyer. It is executed only after all obligations of the sale agreement are fulfilled.💡 Key Point: If the sale deed is not properly drafted and registered, your ownership rights are not legally secure.Common Problems People Face Without a Property LawyerHidden Liabilities – Many properties have unpaid loans, tax dues, or legal disputes. Buyers discover them only after purchase.Defective Titles – If the seller is not the real owner or if the property has multiple claimants, the sale deed can be challenged in court.Unclear Clauses – Vague language in the sale agreement can lead to disputes over possession, payment, or construction delays.Fraudulent Sales – Cases of fake documents, forged signatures, and double sales are common.Registration Issues – Errors in stamp duty, witness details, or registration can render the deed invalid.👉 Solution: A property lawyer conducts thorough due diligence, drafts foolproof agreements, and ensures your rights are protected.Role of a Property Lawyer in Drafting a Sale AgreementTitle Verification – Ensures that the seller has a clear, marketable title to the property.Encumbrance Check – Verifies whether the property is free from loans, mortgages, or litigation.Custom Drafting – Tailors clauses to protect the buyer’s or seller’s interest (payment schedule, penalty clauses, force majeure, etc.).Compliance with Law – Ensures the agreement follows provisions under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, Transfer of Property Act, 1882, and RERA (for under-construction projects).Safeguard Against Defaults – Drafts clear remedies if either party defaults.Role of a Property Lawyer in Drafting & Verifying a Sale DeedDrafting Ownership Transfer Clauses – Ensures that the rights, title, and interest are properly transferred.Stamp Duty & Registration – Calculates exact stamp duty and ensures proper registration under the Registration Act, 1908.Verification of Property Details – Correct description of property (survey no., boundaries, area, municipal records).Witness & Execution Formalities – Ensures that execution is legally valid with witnesses and signatures.Avoiding Future Disputes – Drafts clear indemnity and possession clauses to prevent litigation.Case Laws Highlighting Importance of Proper Sale DeedsSuraj Lamp & Industries Pvt. Ltd. v. State of Haryana (2011) 14 SCC 729The Supreme Court held that property transfer can only be done by a registered sale deed, not by GPA or agreement alone.Hardev Singh v. Gurmail Singh (2007) 2 SCC 404Court clarified that mere possession under an agreement does not give ownership rights; only a registered sale deed can.K.B. Saha & Sons Pvt. Ltd. v. Development Consultant Ltd. (2008) 8 SCC 564Highlighted that vague or incomplete clauses in property documents can cause disputes and litigation.💡 Takeaway: A poorly drafted or unregistered sale deed is a legal risk. Always use a property lawyer.How Property Lawyers Prevent FraudConducting a search in land records office for encumbrances.Checking mutation records and municipal approvals.Verifying RERA registration for under-construction projects.Scrutinizing previous chain of documents to ensure no breaks in ownership.Cross-checking with bank records if property is mortgaged.✨ Don’t risk your hard-earned money. Secure your property deal with KHA Advocates – experts in property law. From drafting to registration, we ensure a safe, transparent, and hassle-free property transaction.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)Q1: Can I buy property without a sale agreement?No. A sale agreement is essential to record terms before executing the final sale deed.Q2: Is notarization enough instead of registration?No. Only a registered sale deed under the Registration Act, 1908, gives you legal ownership.Q3: Can I draft my own sale deed?Technically yes, but it is risky. Property law is complex. Errors can lead to disputes or even cancellation of the sale.Q4: How much does a property lawyer charge for sale deed drafting?Charges vary depending on complexity, location, and property value. At KHA Advocates, we provide cost-effective, transparent legal services.Q5: What if the seller refuses to execute the sale deed after agreement?You can file a Suit for Specific Performance under the Specific Relief Act, 1963. A lawyer will represent you in court.Contact KHA Advocates — Your Property Law Partner📍 Office: KHA Advocates – Property & Real Estate Legal Services📞 Phone : (+91) 94-777-5-888-5📞 WhatsApp: (+91) 8101-555-666📧 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in🌐 Website: www.khaadvocates.com🔗 Quick Appointment Link: https://khaadvocates.com/book-consultation👉 Call us today to book a consultation with our expert property lawyers before signing your sale agreement or sale deed.
Read More
🔹 IntroductionBuying property in New Town, Kolkata is a dream for many. But property registration is not just paperwork — it’s a legal safeguard that determines whether your investment is truly secure. A single mistake can cost you ownership rights, money, and years in court battles.👉 This is why you need a Property Registration Lawyer — to make sure your purchase is legally valid, dispute-free, and future-proof.🔹 What is Property Registration?📖 Under the Registration Act, 1908, property transactions above ₹100 must be registered.📌 Registration = official proof of ownership.📌 Without registration = property has no legal value.In West Bengal, registration also requires compliance with the Stamp Act & Registration Rules.⚠️ Problems Buyers Face Without a Lawyer🚫 Fake/forged documents from sellers🚫 Property under litigation or mortgage🚫 Wrong calculation of stamp duty → penalties🚫 Poorly drafted Sale Deed favoring seller🚫 Encroachment & ownership disputes👉 Solution: Hire a lawyer for due diligence + drafting + registration.🔹 How a Property Registration Lawyer Helps YouA Property Registration Lawyer provides end-to-end support in:a) Title Verification & Due DiligenceChecking original ownership documents (deed, khatian, mutation, tax receipts).Ensuring the property is free from litigation, mortgage, or encumbrance.Searching records at the Sub-Registrar’s office.b) Drafting & Reviewing the Sale DeedCustomizing clauses to protect the buyer’s rights.Ensuring there is no vague language that may favor the seller.Including indemnity clauses against future disputes.c) Stamp Duty & RegistrationCorrectly calculating stamp duty and fees under West Bengal Stamp Act.Filing the necessary documents with the Sub-Registrar.d) Execution & HandoverEnsuring smooth registration before the registering officer.Obtaining the certified copy of the registered deed.Advising on mutation and municipal tax transfer post-registration.Let's Summarise for you ✅ Title Verification – checks deeds, khatian, mutation, encumbrances✅ Drafting Sale Deed – buyer-friendly clauses, indemnity terms✅ Stamp Duty & Fees – accurate calculation under WB law✅ Registration Process – smooth execution at Sub-Registrar’s office✅ Post-registration – mutation, tax transfer, possession⚖️ Case Laws You Must KnowSuraj Lamp & Industries v. State of Haryana (2011) – Only a registered deed transfers ownership.K.B. Saha & Sons v. Development Consultant Ltd. (2008) – Unregistered documents = no legal proof of ownership.👉 Moral: Without proper legal registration, you don’t own the property.🏙️ Why Special Care in New Town, Kolkata?Most properties in New Town are leasehold under HIDCO.⚠️ Risks:Government permission needed for transferLease restrictions applyWrong drafting = cancellation of allotment👉 Only a lawyer experienced in HIDCO leasehold rules can protect you.✅ How We Help at KHA Advocates🔹 Title search + due diligence🔹 Custom deed drafting🔹 Registration at Sub-Registrar’s office🔹 NRI buyer assistance via Power of Attorney🔹 Post-registration services (mutation, tax, possession)💡 We make property registration 100% safe, legal, and stress-free.❓ FAQsQ1: Is a lawyer mandatory for property registration?➡ No, but without one, you risk fraud & defective deeds.Q2: Can NRIs register without visiting India?➡ Yes, via Power of Attorney.Q3: How long does registration take?➡ 2–4 weeks depending on clearances.📞 Contact Us TodayDon’t risk your dream home or investment. Protect it with expert legal help.📲 Call: (+91) 94-777-5-888-5📲 WhatsApp: (+91) 8101-555-666📧 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in🌐 Website: www.khaadvocates.com🔗 Book Appointment: https://khaadvocates.com/book-consultationProperty registration is the foundation of ownership. In places like New Town, Kolkata, where leasehold rules make transactions tricky, hiring a Property Registration Lawyer ensures your investment is safe, legal, and hassle-free.👉 Choose smart. Choose legal security. Choose KHA Advocates.
Read More
IntroductionBuying your dream home is one of the biggest financial and emotional decisions of life. Many buyers, especially first-time buyers, are drawn towards under-construction flats or apartments because they are often cheaper than ready-to-move-in properties and come with flexible payment options. However, under-construction properties also involve higher risks, such as project delays, legal disputes, or even fraud.As a buyer, knowing the legal process, safety measures, and essential do’s & don’ts can help you secure your investment and avoid unnecessary stress.At KHA Advocates, we assist property buyers with end-to-end legal support, from due diligence to registration, ensuring you buy your home with complete confidence.Step-by-Step Legal Process of Buying an Under-Construction Flat1. Check RERA RegistrationVisit your state’s RERA (Real Estate Regulatory Authority) portal.Verify whether the project is registered.Check the builder’s past projects, timelines, and compliance status.👉 Why it matters: Only RERA-approved projects provide legal safeguards for buyers.2. Verify Builder’s Title & ApprovalsConfirm the builder has clear ownership or development rights over the land.Check approvals from local authorities (municipality, fire, environmental clearance, etc.).👉 Why it matters: Buying from a builder without proper approvals can lead to cancellation of the project.3. Examine the Builder-Buyer AgreementCarefully review clauses on possession date, construction linked payments, cancellation, and refund policies.Look for hidden charges (maintenance, parking, club membership, etc.).👉 Why it matters: This agreement defines your rights – a lawyer can help negotiate unfavorable terms.4. Payment & Home Loan ProcedurePayments should follow the construction-linked plan and not exceed 10% before agreement registration (as per RERA).For home loans, banks conduct their due diligence – but don’t rely solely on bank approvals.5. Registration of Agreement for SaleLegally register your agreement at the Sub-Registrar’s office.Pay applicable stamp duty & registration charges.6. Possession & Occupancy CertificateBefore possession, check for Occupancy Certificate (OC) and Completion Certificate (CC).Without these, the property is legally incomplete.Safety Measures Before Booking an Under-Construction Flat✅ Check Builder’s Reputation – Past delays, litigation, financial standing.✅ Verify Carpet Area – RERA mandates selling on carpet area, not super built-up.✅ Escrow Account Compliance – Ensure builder deposits 70% of buyer’s funds in RERA account.✅ Timely Updates – RERA requires builders to provide construction progress updates online.✅ Legal Scrutiny of All Documents – Hire a property lawyer to verify every paper.Do’s & Don’ts List for Buyers✅ Do’s:Do verify the project’s RERA registration.Do conduct a legal title check of the land.Do hire a real estate lawyer for document vetting.Do keep all receipts, agreements, and builder communication in writing.Do check for hidden charges like GST, maintenance, parking.❌ Don’ts:Don’t rely solely on the builder’s brochure or promises.Don’t pay more than 10% of the cost before agreement registration.Don’t skip checking OC & CC before taking possession.Don’t ignore the fine print in the builder-buyer agreement.Don’t book based only on verbal assurances or flashy advertisements.Case Study: Buyers Saved by Legal Due DiligenceA group of buyers in Kolkata booked flats in an under-construction project that was heavily advertised. Our team at KHA Advocates was approached for due diligence. Upon inspection, we found that:The land title had a pending litigation.The builder had failed to secure environmental clearance.By acting early, the buyers avoided investing in a risky project and redirected their funds into a RERA-compliant development.👉 Lesson: A small investment in legal checks can save you from losing your life savings.Why You Need a Real Estate Lawyer for Under-Construction PropertiesContract Protection – Lawyers help negotiate builder-buyer agreements to protect your interests.Fraud Prevention – Prevents scams by verifying builder credentials and land titles.Compliance Checks – Ensures approvals and sanctions are in place.Dispute Resolution – Quick legal recourse in case of delays or defaults.Peace of Mind – Focus on your dream home while your lawyer safeguards your investment.ConclusionBuying an under-construction flat can be rewarding, but it comes with risks that only expert legal guidance can minimize. Don’t let hidden clauses, delayed possession, or fraud turn your dream home into a nightmare.At KHA Advocates, we specialize in property law and real estate legal services. From document verification to dispute resolution, we ensure that your home-buying journey is secure, transparent, and stress-free.👉 Build your dream home with confidence – Partner with KHA Advocates today!📞 Contact Us: +91-9477758885📧 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in📍 Location: New Town, Near CC2, Kolkata, West Bengal, India🌐 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com
Read More
IntroductionThe real estate industry is one of the most lucrative yet legally complex sectors in India. Every deal—whether it’s the purchase of land, the sale of flats, or large-scale township development—comes with a web of contracts, regulatory approvals, and compliance obligations. For real estate agents and developers, success is not just about finding the right buyer or executing a project; it’s about ensuring that every step is legally secure.This is why having an expert real estate lawyer on your side is no longer optional—it is a necessity. At KHA Advocates, we specialize in providing end-to-end legal solutions to real estate agents, developers, and investors, ensuring smooth transactions, risk mitigation, and faster deal closures.Why Real Estate Lawyers Are Indispensable1. Property Title Verification & Due DiligenceBefore finalizing any property deal, it is crucial to verify ownership and legal status.Our lawyers conduct title searches, encumbrance checks, mutation record verification, and litigation status checks.This ensures that developers and agents never risk selling or promoting disputed properties.2. Drafting & Reviewing AgreementsReal estate transactions involve Agreements to Sell, Sale Deeds, Development Agreements, Lease Deeds, RERA-compliant builder-buyer agreements, and Joint Venture Contracts.A minor error in drafting can lead to years of litigation or financial loss.Our expert lawyers ensure every clause safeguards your interest, prevents disputes, and complies with Indian property law.3. RERA Compliance & Regulatory ApprovalsWith the introduction of RERA (Real Estate Regulatory Authority), developers must comply with stringent guidelines before advertising or selling projects.We assist in RERA registration, quarterly compliance, buyer dispute defense, and regulatory filings.Real estate agents and developers who work with us avoid penalties, project delays, and reputational risks.4. Dispute Resolution & Litigation SupportProperty disputes are common—ranging from delayed possession claims, land acquisition disputes, buyer complaints, or contractual disagreements.Our legal team represents clients before RERA, Consumer Courts, Civil Courts, High Courts, and Arbitration Tribunals.Having a strong legal partner ensures disputes are handled strategically and quickly, protecting your brand reputation.5. Taxation & Financial StructuringReal estate transactions are heavily taxed through stamp duty, GST, TDS, and capital gains tax.Our lawyers collaborate with tax experts to structure deals in the most tax-efficient way, ensuring compliance while maximizing profits.6. Joint Ventures & Builder CollaborationsMany developers enter into Joint Development Agreements (JDAs) with landowners.Without proper legal safeguards, developers risk losing control or profits.Our team ensures fair drafting, profit-sharing clarity, exit clauses, and dispute resolution mechanisms in such collaborations.7. Faster Deal Closures with Legal BackupA property deal backed by a reputed law firm builds trust among buyers, investors, and financial institutions.When buyers see that all documents are vetted by KHA Advocates, confidence increases, leading to quicker sales and project funding.Why Real Estate Agents & Developers Prefer KHA Advocates✅ End-to-End Support – From due diligence to litigation defense.✅ RERA Specialists – Complete compliance support.✅ Deal Structuring Experts – Tax-efficient, legally sound transactions.✅ Strong Dispute Defense – Representation across courts and tribunals.✅ Trusted by Investors & Homebuyers – Our legal certification enhances credibility.Example Case StudyA leading developer in Kolkata faced a buyer dispute over delayed possession. The case went to RERA, where the buyer demanded refund with interest. By strategically defending the matter, KHA Advocates helped the developer avoid a ₹2 crore liability and negotiated an amicable settlement, saving both reputation and money.ConclusionIn today’s competitive real estate market, having an expert real estate lawyer is not a luxury—it’s a business strategy. From compliance to dispute resolution, lawyers ensure that every deal is legally sound, every agreement is enforceable, and every project runs without costly interruptions.At KHA Advocates, we pride ourselves on being the legal backbone for real estate agents and developers, empowering them to focus on growth while we safeguard their legal interests.Let's Connect with an Expert👉 Are you a real estate agent or developer looking for a trusted legal partner?👉 Do you want hassle-free deal closures, RERA compliance, and dispute protection?📞 Contact KHA Advocates today and let our expert real estate lawyers secure your deals.
Read More
IntroductionThe Enemy Property Act, 1968 has often been in the news due to high-profile property disputes. One of the most talked-about cases involves Bollywood actor Saif Ali Khan and the prestigious Pataudi Estate. While many see this as a family inheritance matter, legally it is much more complicated, as the Enemy Property Act directly governs whether heirs like Saif can claim ownership of certain ancestral assets.This blog explores the legal perspective on the Enemy Property Act, its relevance to the Pataudi Estate dispute, and how it impacted Saif Ali Khan’s inheritance rights.What is the Enemy Property Act?The Enemy Property Act, 1968 was enacted by the Government of India after the Indo-Pak wars of 1965 and 1971. It essentially deals with properties left behind in India by people who migrated to Pakistan or China during these wars.Such properties were taken over by the Custodian of Enemy Property for India.Heirs of those who migrated were barred from claiming ownership rights.Even Indian citizens related to the “enemy” were restricted from succession to such properties.The law was strengthened further in 2017 through an amendment, making it clear that no heir of an enemy can inherit such property, even if they are Indian citizens.The Pataudi Estate Dispute – BackgroundThe Pataudi family, a prominent royal household in Haryana, traces its lineage back to Nawab Iftikhar Ali Khan and later Nawab Mansoor Ali Khan Pataudi. The estate included prime landholdings, palaces, and ancestral properties.The controversy began when it was argued that certain portions of the Pataudi Estate fell within the ambit of the Enemy Property Act due to the migration of some family members to Pakistan.This created legal hurdles in the inheritance of Saif Ali Khan, son of Mansoor Ali Khan Pataudi and Sharmila Tagore, despite him being an Indian citizen and legal heir.How the Enemy Property Act Affected the Pataudi Estate The legal complications arose because: • Some of Saif Ali Khan’s relatives, including family members connected to Bhopal and Hyderabad princely states, had migrated to Pakistan. • Under the Enemy Property Act, properties belonging to those relatives were considered enemy property. • This meant that even Indian-born heirs like Saif Ali Khan could not automatically inherit certain ancestral properties. Thus, while Saif was declared the legal heir to parts of the Pataudi Estate, the Enemy Property Act restricted his rights over portions of the ancestral property. How Did This Affect Saif Ali Khan? The direct impact of the Enemy Property Act on Saif Ali Khan was significant: 1. Inheritance Restriction – Saif could not freely inherit all properties linked to his ancestors because the law prohibited transfer of enemy property to heirs. 2. Legal Disputes & Delays – The Pataudi family faced litigation and government intervention, leading to a prolonged battle to establish ownership rights. 3. Loss of Royal Assets – Despite being the legal heir, Saif’s rights over parts of the estate were curtailed, preventing him from exercising full control. 4. Symbolic Loss of Heritage – For Saif, the dispute was not only about property value but also about ancestral pride and royal legacy. This demonstrates how even celebrity heirs are not immune to the far-reaching consequences of the Enemy Property ActLegal Perspective on the CaseFrom a legal standpoint, the dispute highlights several critical issues:Conflict between Succession Laws & Enemy Property ActNormally, under the Hindu Succession Act or personal laws, a son inherits his father’s property.However, the Enemy Property Act overrides succession rights, making heirs powerless if the property is classified as enemy property.Doctrine of Public PolicyThe Act is based on national interest, preventing properties linked to “enemies” from being exploited.But, in practice, it often impacts Indian citizens like Saif Ali Khan, raising concerns of fairness.Judicial InterpretationsIndian courts have consistently upheld the supremacy of the Act, limiting the scope of inheritance claims.This shows how special laws override general inheritance provisions.Lessons for Property Owners and HeirsThe Pataudi Estate dispute serves as a cautionary tale for families dealing with ancestral properties. Key lessons include:Title Verification is Crucial – Before claiming or buying any property, ensure it is not under the Enemy Property Act or other restrictions.Legal Documentation Matters – Proper succession deeds, wills, and title clearances can reduce future disputes.Seek Legal Expertise Early – Corporate lawyers and property law experts can prevent disputes from escalating into decades-long battles.NRI Families Must Be Extra Careful – Many NRIs unknowingly inherit properties linked to enemy properties, exposing them to long litigation.How Our Law Firm Can HelpAt KHA Advocates, we specialize in:Property Title Verification – Ensuring properties are free from legal encumbrances before purchase or transfer.Inheritance & Succession Advisory – Drafting wills, succession certificates, and family settlements to secure property rights.Dispute Resolution & Litigation Support – Representing clients in property disputes, including those under special laws like the Enemy Property Act.NRI Property Services – Helping NRIs manage, protect, and transfer their properties in India.If you’re facing property disputes or inheritance complications, our expert property lawyers can safeguard your rights.ConclusionThe Enemy Property Act was designed to protect national interests but has had profound implications on individual inheritance rights. The Saif Ali Khan Pataudi Estate dispute is a high-profile example of how this law can prevent rightful heirs from accessing ancestral property.For business owners, heirs, and NRIs, the key takeaway is clear: always seek legal due diligence and expert advice before claiming, buying, or transferring property👉 If you need guidance on property disputes, connect with KHA Advocates today and protect your rights before it’s too late.
Read More
Buying land in West Bengal can be rewarding—but only if you get the legal basics right. This guide walks you through due-diligence steps, must-know rules under Bengal laws, and the current stamp duty & registration charges, with quick examples, case-law checkpoints, and a simple checklist you can use before you sign.1) Start with a Clean Title: What to Verifya) Chain of Title (minimum 30 years).Collect all prior deeds (sale, gift, partition, exchange) and compare RS/LR Dag & Khatian numbers, Mouza, and area across documents.Ensure there are no gaps in the chain and that every transferor actually had the right to sell.b) Encumbrance Check.Obtain an Encumbrance Certificate and search the Sub-Registrar’s records for mortgages, lis pendens, attachments, court orders, or ongoing disputes.c) Mutation vs. Ownership.Mutation (name change in Record-of-Rights/Porcha) is important for tax and utilities but it doesn’t prove ownership. Courts repeatedly hold that mutation entries are only for fiscal purposes and don’t create or extinguish title. d) Land Use & Conversion (Agricultural to Non-Agricultural).For agricultural plots, check conversion permissions (where applicable) and land-use restrictions before development.Verify local plans, zoning, road-widening reservations, waterbodies, thika land issues, coastal or forest restrictions, etc.e) Possession & Boundaries.Conduct a site survey with a licensed surveyor; match ground boundaries with revenue maps and deeds.Confirm access/right of way is legal and undisputed.f) Special Estates & Leaseholds.In areas like Bidhannagar (Salt Lake) and some industrial estates, you’re often buying leasehold rights with transfer conditions and authority permissions. Review allotment letters, lease deeds, and transfer policies carefully.Case-law guardrail: The Supreme Court in Suraj Lamp & Industries v. State of Haryana (2011) held that GPA/Agreement-to-Sell/Will (“SA/GPA/Will”) transactions do not convey title; only a registered conveyance deed transfers ownership of immovable property. Don’t rely on “GPA sales.” 2) Agreements & Documents You’ll Typically NeedTitle Verification Report (by your lawyer, post record and site checks)Agreement for Sale (with detailed reps/warranties; attach a schedule and accurate site plan)No-objection certificates/permissions (as applicable—ULC/ceiling compliance history, conversion NOC, municipal/revenue clearances, society/lessor consent)Registered Sale Deed at the jurisdictional Sub-Registrar office (mandatory to pass title). Recent Supreme Court guidance re-affirms that documents requiring registration are inadmissible to convey title if unregistered. 3) Stamp Duty & Registration Charges in West Bengal (2025)Use Stamp Duty Calculator developed by KhA AdvocatesImportant policy updates:West Bengal withdrew the temporary 2% stamp duty rebate and 10% circle-rate reduction from July 1, 2024 (initially introduced in Oct 2021). Always budget at full rates now. From January 17, 2024, the State announced stamp duty assessment on carpet area, not super built-up area (and simultaneously revised circle rates). Expect operational nuances while authorities refine forms. How to estimate online: Use the MV/SD/RF Calculator on the West Bengal Registration portal (select “Stamp Duty & Registration Fee”). 4) Bengal-Specific Pitfalls (and how to avoid them)Ceiling & Tenancy footprints: Trace historic land ceiling proceedings/regularizations and tenancy (bargadar) claims.Waterbodies/Khaitan descriptors: If the RoR shows doba, pukur, khal etc., special restrictions may apply; converting and filling may be prohibited without permissions.Thika & Khas Mahal land: Extra layers of consent/eligibility can apply—get a targeted legal opinion.Leasehold in planned townships: Check transfer charges, lessor’s prior consent, and lock-in conditions.Set-offs and approach roads: Verify right of way is recorded; don’t assume a neighbor’s path is public.“GPA sale” or “Notary deed” shortcuts: Avoid—no title passes without a registered conveyance. 5) Micro-Checklist Before You Pay Token Money✅ Title search (30 years) with encumbrance & litigation scan✅ RoR/Porcha & mutation status matched to deeds (knowing mutation ≠ title) ✅ Site survey & boundary match (with LR/RS maps)✅ Land use & conversion permissions verified✅ Utility dues & property tax updated; indemnities for past dues✅ No pending acquisition/road widening reservations✅ Drafting of robust Agreement for Sale (clear reps/warranties, indemnities, timelines, default & refund clauses)✅ Final deed: register at proper SRO; pay stamp duty + 1% registration via GRIPS/IGR portals; collect e-challans & final registered copy. 6) Case-Law Corner (What it means for you)Mutation ≠ Ownership. Courts consistently reiterate that mutation is fiscal/administrative and does not confer title—use it to update records and pay taxes, not as proof of ownership. Only a Registered Conveyance Passes Title. The Supreme Court in Suraj Lamp (2011) held SA/GPA/Willpathways do not transfer ownership. Insist on a registered sale deed. Recent Supreme Court orders continue to underscore Sections 17 & 49 of the Registration Act, 1908—unregistered documents that require registration are inadmissible to convey title. 7) FAQsQ1. What are the current stamp duty and registration rates in West Bengal?A. Registration fee is 1%. Stamp duty varies by location and value slab (e.g., rural 3–4%, urban 4–5% generally; Kolkata/Howrah slabs often reflect 6–7% bands). Use the IGR calculator for your exact local body and property value. Q2. Is the 2% stamp duty rebate still available?A. No. It ended June 30, 2024; normal rates apply from July 1, 2024. Q3. Is stamp duty based on carpet area or super built-up?A. The State announced assessment on carpet area (with other adjustments like circle-rate revisions). Expect implementation nuances; always check the latest form and local SRO practice. Q4. Can I buy through GPA/ATS to save time or cost?A. Avoid. No title passes without a registered conveyance. Q5. Do women or senior citizens get a concession in Bengal?A. Unlike some states, no general gender-based concession is provided; check if any time-bound schemes are notified. Use the IGR calculator for the precise figure. 8) How KHA ADVOCATES Helps You Close Safely (and Save Money)Title & Litigation Deep-Dive: We run a 30-year title audit, encumbrance search, and suit/attachment scan so you don’t inherit hidden risks.Structuring & Tax-smart Drafting: From Agreement for Sale to Sale Deed, we build iron-clad clauses(indemnities, default matrix, delayed possession compensation, price-protection) and align TDS, GST (ifany) and stamp duty planning to avoid penalties.Regulatory Navigation: Conversion, lessor/society permissions, RERA alignment, and municipal compliances—done end-to-end.Registration Day Concierge: Slot booking, GRIPS/IGR e-payments, document checks, witness coordination, and smooth execution at the SRO.'After-care: Mutation applications, tax meter shift, and record updates so your ownership reflects everywhere that matters.Free 15-minute Consultation: Planning to buy land in Kolkata, Howrah, Salt Lake, Siliguri, Durgapur or across Bengal? Book a call with KHA ADVOCATES to get a quick duty estimate + red-flag review of the property before you commit.9) Final TakeawaysDon’t rely on mutation as ownership proof; rely on clear title + registered deed. Budget stamp duty + 1% registration at post-rebate rates (effective July 1, 2024). Use the official calculator for exact numbers by local body and value, and get documents vetted before you pay token money. Need a precise stamp duty & fee calculation for your plot—and a same-day document red-flag review?Message KHA ADVOCATES now. One guided call can save you lakhs and months of stress.
Read More
IntroductionContracts are the backbone of every business relationship. Whether you’re a startup signing your first vendor agreement or a corporation negotiating a multi-crore deal, a poorly drafted contract can lead to disputes, losses, and even litigation. In India, contract drafting is governed primarily by the Indian Contract Act, 1872, along with provisions of the Indian Stamp Act, 1899, and relevant judgments by the Supreme Court and High Courts.In this blog, we’ll explore the most common mistakes made during contract drafting, legal consequences, landmark judgments, and practical tips on how to avoid them.1. Vague or Ambiguous ClausesMistake: Using unclear terms such as “reasonable time,” “best efforts,” or “mutual understanding.”Consequence: Leads to multiple interpretations and disputes.Case Law: ONGC v. Saw Pipes Ltd. (2003) – The Supreme Court held that vague clauses can render contracts unenforceable if they lack certainty.Solution: Always use precise, measurable language. For example, instead of “deliver goods on time,” specify “deliver 500 units within 30 days.”2. Missing Jurisdiction & Governing Law ClausesMistake: Failing to specify which court or state laws will govern disputes.Consequence: Parties may file cases in multiple jurisdictions, leading to unnecessary litigation.Case Law: Swastik Gases Pvt. Ltd. v. Indian Oil Corporation Ltd. (2013) – The Supreme Court emphasized the importance of jurisdiction clauses.Solution: Insert a clear clause like: “This Agreement shall be governed by the laws of India, and courts at Kolkata shall have exclusive jurisdiction.”3. Ignoring Stamp Duty & Registration RequirementsMistake: Contracts like leases, partnerships, or property agreements often remain unstamped or unregistered.Consequence: Courts may refuse to admit such documents as evidence.Law: Indian Stamp Act, 1899 and Registration Act, 1908.Example: An unstamped lease deed exceeding 12 months can be declared invalid.Solution: Always calculate proper stamp duty and register agreements wherever required.4. Skipping Termination & Exit ClausesMistake: Not defining conditions for termination or exit of parties.Consequence: Leads to endless disputes when parties want to exit.Case Law: Tata Consultancy Services Ltd. v. Cyrus Investments Pvt. Ltd. (2021) – The importance of clear exit clauses in shareholder agreements was highlighted.Solution: Define termination events (breach, insolvency, force majeure) and lay down notice periods, penalties, and handover procedures.5. Not Defining Payment Terms ClearlyMistake: Contracts state “payment shall be made promptly” without defining mode, due date, or late fee.Consequence: Disputes over payment delays and penalties.Law: Indian Contract Act, 1872 (Section 73 – Compensation for Breach of Contract).Solution: Specify “Payment of ₹10,00,000 shall be made via bank transfer within 15 days of invoice, with 12% interest applicable on delays.”6. Boilerplate Copy-Paste Contracts Mistake: Using internet templates without customization.Consequence: Many clauses may be irrelevant, illegal, or contradictory.Case Study: A startup copied an NDA template online, which did not comply with Indian law. During litigation, the court rejected parts of the NDA.Solution: Always customize contracts based on Indian law, industry, and party requirements.7. Overlooking Force Majeure & Pandemic ClausesMistake: Not including provisions for unforeseen events like pandemics, wars, or natural disasters.Case Law: Halliburton Offshore Services v. Vedanta Ltd. (2020, Delhi HC) – The court recognized COVID-19 as a force majeure event.Solution: Define force majeure events, notification timelines, and consequences (suspension or termination).Practical Tips for Safe Contract DraftingHire a Lawyer: Professional vetting prevents loopholes.Review Twice: Both parties should review drafts carefully.Update Regularly: Revise old contracts to include latest laws and judgments.Use Clear Language: Avoid jargon, keep it simple.FAQs on Contract DraftingQ1. Is an oral contract valid in India?Yes, oral contracts are valid under the Indian Contract Act, 1872, but difficult to prove in court. Always prefer written contracts.Q2. What makes a contract legally enforceable in India?Offer, acceptance, lawful consideration, free consent, lawful object, and capacity of parties.Q3. Can a contract be on plain paper without stamp duty?Yes, it’s valid but may not be admissible in court without proper stamping.Q4. What happens if a contract has a missing clause?Courts may interpret it against the drafter, leading to unfavorable judgments.Q5. How can startups ensure safe contract drafting?By consulting a corporate lawyer to draft customized agreements like Founders’ Agreement, Shareholders’ Agreement, and Employment Contracts.Q6. Do contracts need witnesses?Not always. Only certain agreements like property deeds, wills, or surety bonds need attestation.Q7. Can e-contracts and digital signatures be used in India?Yes, under the Information Technology Act, 2000, e-signatures and e-contracts are legally valid.At KHA Advocates, we specialize in contract drafting, vetting, and negotiation for startups, corporates, and individuals. Our expert lawyers ensure your agreements are legally enforceable, customized to your needs, and dispute-proof.👉 Avoid costly litigation – Book a consultation with KHA Advocates today!
Read More
Introduction: Why RERA Matters for New AgentsIf you’re a real estate agent with less than three years of experience, you’ve probably heard the term RERA thrown around in conversations, training programs, and even client meetings. The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 was introduced to bring transparency, accountability, and fairness to India’s real estate sector.For agents, RERA is not just a legal formality—it’s your license to operate, build trust, and close deals confidently. In fact, RERA compliance can be your biggest selling point when winning over clients.This guide will walk you through everything you need to know about RERA compliance, with practical tips, legal insights, and real-world advice tailored for agents like you.What is RERA and Why Should Agents Care?RERA was enacted to protect homebuyers and regulate the real estate industry. For agents, it:Makes registration mandatory to operate legally.Requires disclosure of property details before selling.Ensures ethical dealing with both buyers and developers.Failing to comply can result in hefty penalties or even being barred from business. On the flip side, RERA compliance can boost your credibility and help you close more sales.Step-by-Step RERA Compliance Checklist for Agents1. Register Yourself as a RERA AgentWhy? It’s the law. You cannot facilitate property sales without RERA registration.How? Visit your state’s RERA website, fill out the application form, upload required documents, and pay the registration fee.Tip: Always keep your registration number handy—it builds instant trust with clients.2. Understand Your State’s RERA RulesEach state has its own RERA authority and rules. For example, WBRERA in West Bengal, etc.Action Step: Bookmark your state’s RERA website and check for rule updates regularly.Benefit: Staying updated means you won’t accidentally violate new regulations.3. Work Only with Registered ProjectsSelling an unregistered project is a major violation. Always check the RERA project registration number before marketing or selling.Tip: Use the RERA portal to verify project details—buyers love agents who show them official proof.4. Disclose Accurate Information to ClientsUnder RERA, you must share all relevant details about a property—pricing, possession timelines, approvals, and amenities.Best Practice: Maintain a property fact sheet for every listing.5. Maintain Transaction RecordsRERA requires agents to keep proper records of transactions.Why? These can protect you in case of disputes.Pro Tip: Digitize your paperwork using cloud storage—it’s safer and faster to retrieve.6. Avoid Misleading AdvertisementsRule: Do not advertise unapproved layouts, amenities, or false possession dates.Example: If possession is 2027, don’t write “Ready in 2 Years” unless confirmed.7. Renew Your RERA Registration on TimeRERA registrations have an expiry date—usually 5 years, but it varies by state.Tip: Set calendar reminders for renewal at least 3 months in advance.8. Act as a Neutral FacilitatorRERA recognizes agents as intermediaries, not salespeople for one party.Ethics Tip: Always ensure fairness between the buyer and seller.9. Stay Updated with RERA AmendmentsThe law is evolving. Attend RERA workshops, webinars, or legal training to keep learning.Benefit: Your knowledge will set you apart from other new agents.10. Partner with a Legal MentorIf you’re new, navigating compliance can be overwhelming. Working with a law firm specializing in RERA can save you from costly mistakes and even speed up your deal closures.Common RERA Mistakes New Agents MakeSkipping registration to avoid fees.Not verifying projects before selling.Making verbal promises that can’t be kept.Ignoring renewal dates for registration.Not keeping proper documentation of transactions.Avoiding these mistakes will keep your record clean and your reputation strong.How RERA Compliance Helps You Win More ClientsBuilds trust – Buyers feel safer dealing with registered agents.Differentiates you – Many agents still operate without full compliance.Protects you legally – Compliance shields you from penalties and lawsuits.Boosts referrals – Happy, protected clients recommend you to others.FAQ – RERA for New Real Estate AgentsQ1. Do I need RERA registration if I only deal in rentals?A: No, RERA applies to property sales, not rentals. But check your state’s rules for exceptions.Q2. How much does RERA registration cost?A: Fees vary by state—usually between ₹25,000 for individuals.Q3. Can I operate in multiple states with one RERA license?A: No, you need separate registration for each state.Q4. What happens if I sell an unregistered project?A: You can face heavy fines or even imprisonment. Always verify before selling.Q5. How long does RERA registration take?A: Usually 15–30 days, depending on state processing times.Final Thoughts – Your Compliance is Your StrengthAs a new agent, it’s tempting to focus only on closing deals quickly, but in today’s regulated market, compliance is your competitive edge. Buyers and developers want to work with agents they can trust—and RERA compliance is proof of your professionalism.Don’t see RERA as a hurdle; see it as a business tool that helps you stand out in a crowded market.Let’s Build Your RERA-Ready CareerAt KHA Advocates, we act as your legal mentor—guiding you through RERA registration, project verification, agreement vetting, and compliance training.Whether you’re a new broker or a growing agency, our legal support ensures you operate 100% within the law while building a trustworthy brand.📞 Call us today at 9832-555-666 or 📧 email us at contact@khaadvocates.in to start your RERA-compliant journey.
Read More
Booking a flat—especially in an under-construction or newly launched project—is a big step for any property buyer or investor. While glossy brochures, virtual tours, and builder promises may look appealing, failing to conduct a legal due diligence check before booking can result in financial losses, stalled projects, or court battles.At KHA ADVOCATES, we help buyers—especially first-timers and NRIs—safeguard their investments with comprehensive legal support. This guide lays out a legal checklist to follow before you pay that booking amount.1. Check if the Builder is RERA RegisteredWhy it matters:Under the Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016, all builders must register their residential projects (above a certain size) with RERA.What to verify:RERA Registration NumberProject details on your state’s RERA websiteCompletion timeline and approvalsTip: Visit https://rera.gov.in and cross-check project details.📌 KHA Tip: We verify RERA registration and flag any discrepancies before you invest.2. Verify Title of the LandWhy it matters:The builder must legally own or have development rights over the land. If the land title is disputed or not clear, the entire project becomes risky.What to verify:Title Deed and Ownership Chain (30-year verification)Encumbrance Certificate (EC)Lease/Development Agreements (if applicable)📌 KHA Tip: We conduct deep title verification and provide certified legal title reports.3. Check Project Approvals & SanctionsWhy it matters:Without proper municipal and environmental approvals, the builder may face demolition or delay orders. You risk losing time and money.Key approvals to verify:Commencement Certificate (CC)Building Plan Sanction by local authorityEnvironmental Clearance (for large projects)Fire Safety and Airport NOC (if applicable)📌 KHA Tip: We inspect all sanctions and compare them with construction on-ground.4. Examine the Allotment Letter & Builder-Buyer AgreementWhy it matters:These are legally binding documents that define your rights, timelines, penalties, and possession terms.Watch for:Clause on delivery date and delay penaltiesForce majeure clausesEscalation charges or hidden costsRefund/termination terms📌 KHA Tip: We negotiate the Builder-Buyer Agreement and protect you from one-sided terms.5. Understand the Carpet Area ClausesWhy it matters:Builders often quote “super built-up area” to appear cheaper. But you only own the carpet area.Legal point:RERA mandates disclosure of carpet area and its definition.What to check:Clearly mentioned carpet areaLoading % (difference between super built-up and carpet)Agreement mentions area escalation clauses?📌 KHA Tip: We break down the loading percentage and explain your actual usable space.6. Check for Litigations & Pending CasesWhy it matters:Even a high-profile project can have pending disputes or litigation that stalls completion.How to check:Builder’s litigation history (via High Court/SC portals)RERA complaintsConsumer forum or NCLT disputes📌 KHA Tip: We do background checks on builders across legal portals and flag red zones.7. Verify the Builder’s Previous ProjectsWhy it matters:Past delivery record speaks volumes about future reliability.Things to verify:Completion historyQuality of constructionDelay frequencyConsumer complaints📌 KHA Tip: We verify past project delivery and check for blacklisted builders.8. Check Home Loan Pre-Approvals (If Any)Why it matters:If reputed banks have approved loans for the project, it signals that due diligence has been done. Still, it’s not foolproof.Check for:Which banks have approved the projectLoan eligibility termsLoan-to-value ratio offered📌 KHA Tip: We independently verify bank clearance and help you secure home loans at best rates.9. Ensure GST, Stamp Duty, and Tax Implications Are ClearWhy it matters:Tax liabilities, if not properly calculated, can spike your cost by lakhs.What to check:GST applicable for under-construction flats (usually 5% without ITC)Stamp duty & registration chargesTDS (1%) if value exceeds ₹50 lakh📌 KHA Tip: We help optimize your property taxes and legally reduce stamp duty wherever possible.10. Review Possession Timeline & Completion CertificateWhy it matters:You must legally take possession only after receiving the Occupancy Certificate (OC) or Completion Certificate (CC).Ensure:Delivery date is not vagueCompensation clause for delayFinal handover includes OC and NOC from authorities📌 KHA Tip: We ensure legal handover, post-registration compliance, and verify builder’s obligations.🚨 Never Pay in Cash or Unaccounted PaymentsWhy it matters:Any cash transaction is illegal and non-defendable in court. Always insist on full transparency.📌 KHA Tip: We ensure all payments are through legal channels and documented properly.Why Buyers & Investors Choose KHA ADVOCATESAt KHA ADVOCATES, we don’t just “check papers”—we secure your entire property purchase from booking to registration. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or seasoned investor, our services include:✔️ Title Verification (30 years)✔️ Builder-Buyer Agreement Drafting & Review✔️ Property Registration & Mutation✔️ Stamp Duty Optimization✔️ Legal Due Diligence & Litigation Check✔️ Home Loan Legal Support✔️ Dispute Prevention & Litigation📞 Ready to Book a Flat? Don’t Do It Without Legal Backing.📞 Book a Legal Consultation with KHA ADVOCATES👉 Call us now : 94-777-5-888-5👉 WhatsApp: 8101-555-666👉 Email us: contact@khaadvocates.in👉 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com
Read More
IntroductionBuying a property—especially for NRIs or first-time buyers in West Bengal—is often seen as a milestone achievement. However, what’s not visible in glossy brochures and site visits are the hidden charges that can inflate your cost by lakhs. Whether you’re eyeing a premium flat in Salt Lake or an investment property in Durgapur, knowing what lies beneath the surface is crucial to avoid legal and financial pitfalls.At KHA ADVOCATES, we’ve helped hundreds of clients legally uncover and prevent hidden property costs through rigorous legal due diligence, title search, and registration support.⚠️ Common Hidden Charges Most Buyers Overlook1. Legal Scrutiny & Title Due Diligence (Or Lack Thereof)Builders often charge legal processing fees, but these do not include independent title verification. Many NRIs assume the property is “clear,” only to later face disputes.Real Case: A buyer in New Town discovered, post-payment, that the property was under litigation despite having paid legal fees to the builder.✔️ Solution: Always appoint your own property lawyer for due diligence.2. GST on Under-Construction PropertyAs per current law, under-construction properties attract 5% GST (without ITC), while ready-to-move flats are exempt if the completion certificate is received.💡 Tip: Ask for the CC or OC (Occupancy Certificate) to avoid unnecessary tax burdens.3. Car Parking ChargesParking isn’t “free.” Many builders in Kolkata and Salt Lake charge ₹2–6 lakhs for open or covered parking, despite Supreme Court rulings stating parking cannot be sold separately from the flat.📜 Case Reference: Nahalchand Laloochand Pvt Ltd v. Panchali Co-op Housing Society Ltd – SC held that open parking cannot be sold as an independent unit.4. Clubhouse & Maintenance DepositsThese are often presented vaguely as “amenities charges.” In gated communities, builders demand 1–3 years of advance maintenance and non-refundable clubhouse development fees.✔️ Ask for a breakup of maintenance charges and get it in writing.5. Advance Registration ChargesSome developers insist on upfront registration payments. But beware—many delay handing over sale deeds or register in builder’s name first, forcing resale to buyer with double registration fee.✔️ Registration should only happen after OC/CC and full payment clearance.6. Hidden Floor Rise ChargesEven within the same building, rates differ per floor. Builders in Durgapur, Salt Lake, and Alipore may add ₹20–₹100/sqft for “floor rise” without disclosing this early.7. PLC – Preferential Location ChargesCorner flats, park-facing units, or east-facing homes may have added costs. These are negotiable but often hidden until agreement.✔️ Ask early about PLCs. Always include a clause to limit variation in final price.8. Delayed Possession Penalties SkippedAgreements often don’t mention compensation if possession is delayed. Or worse, they include one-sided clauses favoring the builder.📜 RERA mandates a fixed timeline and penalty for delay under West Bengal Housing Industry Regulation Act (WBHIRA).Legal Checklist to Avoid Hidden Charges✅ StepWhat You Must Check🔍 Title VerificationIndependent search of 30+ years of ownership📜 Agreement ClausesClear breakup of GST, PLC, parking, and maintenance🏗️ RERA RegistrationEnsure property is registered on WBHIRA portal🧾 All-Inclusive QuotationAvoid “base price” traps—ask for final cost🖋️ Builder-Buyer AgreementLegally vetted, RERA-compliant contract🧑⚖️ Legal OpinionHire a property lawyer—not builder’s panel advocatePros and Cons: Ready-to-Move vs Under-Construction in West BengalFeatureReady-to-MoveUnder-ConstructionGST✅ No GST❌ 5% GST (no ITC)Hidden ChargesFewerMany (Amenities, Floor rise, PLC)Risk of DelayMinimalHigh without strong contractRegistration TimelineImmediatePost-completionLegal SecurityHighMedium (depends on due diligence)Real-Life Case Study – How Legal Help Saved a Homebuyer ₹5.5 LakhsA client from Baharampur booked a flat in Chinsurah and was asked to pay ₹3 lakhs as “advance clubhouse charges” and ₹2.5 lakhs for “parking rights.” Our legal team reviewed the documents and found both charges illegal under WBHIRA and Supreme Court guidelines. After a formal notice, the builder dropped all additional demands.✔️ Result: Buyer saved ₹5.5 lakhs and got clean registration within 30 days.Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)Q1: Can I refuse to pay parking charges to a builder?Yes, especially if it’s for open parking. Covered parking may be charged nominally but must be included in the sale agreement.Q2: Are these hidden charges legal under RERA/WBHIRA?No. Builders are mandated to disclose all charges up front. Any deviation can be challenged before the WBHIRA authority.Q3: What if the builder delays possession after I’ve paid full amount?Under RERA, you’re entitled to interest compensation or withdrawal with refund. Get a lawyer to enforce this through legal notice or complaint.Why Choose KHA ADVOCATES?Whether you are an NRI, first-time buyer, or investor, our legal team offers:✅ Title Verification & Search Report (30+ Years)✅ Sale Agreement & Deed Drafting✅ Builder-Buyer Agreement Vetting✅ Registration Support across West Bengal✅ RERA Dispute Handling & Legal NoticesWe’ve helped over 100 clients across New Town, Kolkata, Hooghly, Siliguri, and Durgapur avoid hidden traps and legally secure their investment.ConclusionHidden charges aren’t just financial nuisances—they can become legal nightmares. If you’re buying a property in New Town, Salt Lake, Baharampur, or anywhere in West Bengal, make sure your investment is protected with the right legal guidance.Ready to Buy Property in West Bengal?📞 Book a Legal Consultation with KHA ADVOCATES👉 Call us now : 94-777-5-888-5👉 WhatsApp: 8101-555-666👉 Email us: contact@khaadvocates.in👉 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com
Read More
The Real Estate (Regulation and Development) Act, 2016 (RERA) is now the bedrock of homebuyer protection in India. Under RERA, developers must register each project and deposit most buyer funds in an escrow account (at least 70%) for that project . The latest 2024–25 guidelines strengthen this further. For example, MahaRERA’s Order 57/2024 now requires every sale agreement to list all promised amenities (gym, pool, garden, etc.) and their handover dates . This ensures developers clearly communicate project features and timelines to buyers.RERA also enforces tough penalties for delays or defaults. Section 18 of the RERA Act gives buyers the right to exit a project and get a full refund (with interest) if the builder misses possession deadlines . This isn’t just theory: in early 2025, a Karnataka RERA tribunal ordered a builder to return ₹2.56 crore (with interest) to a flat-buyer after a seven-year delay . Likewise, Haryana’s RERA recently held a developer accountable for a decade-long delay, ordering him to refund ₹1.07 crore plus 11.1% interest (total ₹2.26 crore) to the buyer . Builders must also fix structural defects at their own cost for five years after possession, extending warranty protection far beyond older norms.Because of RERA’s enforcement, buyers now see promised homes and amenities materialize more reliably. Developers must commit to fixed delivery dates for every facility – from swimming pools to clubhouses – or face penalties. For instance, Telangana RERA found a Hyderabad project only 20% complete after three years and ordered refunds with 11% interest to all 62 buyers for the delay . Experts note that requiring exact handover dates “adds accountability,” since homebuyers clearly know when to expect each promised feature .Other key safeguards remain in force. By law, 70% of the money you pay to the builder must go only into the RERA-designated account for that project , preventing diversion of funds. Builders cannot advertise or sell flats before RERA approval, and any violations invite penalties or cancellations. Importantly, recent court rulings confirm that homebuyers can pursue remedies under RERA and under consumer-protection laws simultaneously. In short, fraud or delay can no longer be swept under the rug – homebuyers now have multiple legal venues to insist on fair play.While RERA is implemented state-by-state, its core protections are national. In fact, regulators are building a unified national RERA portal to standardize data across all states . Soon, any buyer will log in and see a developer’s entire track record and project status across India. This integrated system will group every project of a builder together (preventing them from hiding bad history under shell entities) . The goal is to give flat buyers one-click access to key project information and quickly flag any non-compliance.Simplified Checklist for Flat Buyers (2025)Verify RERA registration: Always check that your flat’s project and the developer are registered on the state RERA portal. Official RERA websites list project approvals, layout plans and quarterly progress updates. If the builder isn’t RERA-registered, walk away – you lose all legal protection .Review sale agreement disclosures: Confirm the agreement spells out all promised amenities (pool, gym, garden, etc.) and the deadlines for each . New RERA rules require this level of detail. Any major change later needs the consent of two-thirds of homebuyers . If an amenity is promised in marketing, it must be clearly in the contract.Monitor progress and escrow: Ensure 70% of your payments are going into the RERA escrow account (ask the builder or check RERA filings for confirmation). Track construction progress via the RERA portal or status reports. Soon you’ll even be able to use the national RERA platform to compare projects nationwide . Regularly check that the project is meeting its promised milestones.Know your remedies: If possession is delayed, RERA Section 18 guarantees a full refund plus interest on your payments . If you stay invested, you’re entitled to monthly interest for each month of delay. After handover, RERA gives you a 5-year warranty on structural or major defects. Keep all documents and immediately notify the builder (and RERA) of any delays or defects.Use official grievance channels: File a complaint on the RERA portal at the first sign of trouble. State RERAs generally resolve valid cases within a few months once hearings are scheduled. You can also approach a consumer court in parallel. Provide your sale deed, payment receipts and correspondence to strengthen your case.Engage expert help: RERA compliance can be complex for first-time buyers. Consider consulting RERA verification specialists to review the project before booking. Our RERA compliance service can audit the project’s registration, agreements and builder track record against the latest rules. This expert check helps you avoid costly mistakes.Partner with RERA Compliance ExpertsKeeping up with RERA updates and legal paperwork can be daunting. Our firm offers dedicated RERA compliance guidance to simplify the process. We will review all project documents, verify the builder’s RERA registration and ensure every new 2025 guideline is satisfied. We even monitor construction updates and follow up with regulators if needed. By turning a complex legal checklist into step-by-step guidance, we give you peace of mind. With experts on your side, you can confidently move forward with your new home purchase.Key takeaway: RERA 2025 is about transparency and accountability. Use the above checklist before signing any deal. Remember, under RERA delays and omissions now cost the builder – not you – as confirmed by recent rulings . Armed with the latest guidelines and professional support, flat buyers can invest with confidence.Here’s a promotional and lead generation section tailored for your blog article, “New RERA Guidelines Every Flat Buyer Should Be Aware Of (2025 Edition)”, designed to fit seamlessly near the end of the blog and optimized for SEO and conversion:Why Choose KHA ADVOCATES for RERA Compliance & Property Legal Support?At KHA ADVOCATES, we specialize in protecting the rights of NRI clients, first-time homebuyers, and real estate investors across Kolkata, including New Town and Salt Lake. With decades of experience in real estate law, we ensure that your property journey is legally secure, RERA-compliant, and stress-free.Our RERA & Property Legal Services Include:Full RERA Project Verification (West Bengal RERA, pan-India)Sale Agreement & Builder Agreement VettingTracking Escrow & Possession Timeline CommitmentsLegal Due Diligence & Title Search ReportSupport in Filing RERA Complaints & Refund ClaimsRegistration, Stamp Duty, Mutation & HIRA AssistanceWhether you’re booking a ready-to-move apartment in Salt Lake or investing in an under-construction property in New Town, we’ll help you understand:✔ What your builder can and cannot do under RERA✔ Whether your documents meet 2025 legal compliance✔ What your refund or compensation rights are if timelines slip📞 Book a Free Consultation TodayAvoid costly legal pitfalls before you buy. Let KHA ADVOCATES protect your investment with verified property documentation and expert RERA compliance.👉 Call us now : 94-777-5-888-5👉 WhatsApp: 8101-555-666👉 Email us: contact@khaadvocates.in👉 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com👉 Offices: Kolkata | Virtual Consultations for NRIs 🌐🔐 Buying a Flat? The Builder May Promise. We Legally Verify.Stay protected. Stay informed. Partner with KHA ADVOCATES — your trusted legal shield in Indian real estate.
Read More
IntroductionBuying a flat is a milestone. But a critical question arises for every buyer:Should you go for a ready-to-move-in flat or an under-construction property?While both options come with distinct advantages, the legal implications, risks, and due diligence steps differ drastically. This blog breaks down the legal pros and cons of both choices—especially for first-time home buyers, real estate investors, and NRIs planning to invest in areas like New Town, Salt Lake, and Kolkata.✅ Ready-to-Move-in Flats: Legal Pros & ConsA ready-to-move-in flat is one where construction is completed, possession is granted, and the buyer can immediately shift in or start renting it out.Legal Advantages of Ready-to-Move Properties1. Clear Title & Immediate PossessionYou get to verify the actual property ownership, completion certificate, occupancy certificate, and municipal approvals.No uncertainty over possession timelines.2. No GSTAs per current tax laws, GST is not applicable on ready-to-move properties that have received Completion Certificate (CC).3. What You See Is What You GetThe buyer can physically inspect the flat, locality, and building condition—making legal verification easier.4. Easier to Conduct Legal Due DiligenceYour lawyer can perform a property title search, verify the chain of ownership, check mutation, and confirm that the flat is free from encumbrances.Legal Disadvantages of Ready-to-Move Properties1. Higher CostPer square foot prices are typically 10–20% higher than under-construction properties.2. Risk of Illegal ConstructionMany “ready” flats, especially in developing zones like New Town and Rajarhat, are illegally built without proper sanction plans. Without legal verification, you risk demolition or penalties.3. No Time to Rectify Legal IrregularitiesOnce you purchase, any pending litigation, land disputes, or illegalities become your burden.🏗️ Under-Construction Flats: Legal Pros & ConsAn under-construction property is still being developed and usually offers staged payment plans and relatively affordable pricing.Legal Advantages of Under-Construction Properties1. Lower Cost with FlexibilityPrice per square foot is often lower, especially during pre-launch stages.Payment plans are staggered across construction milestones, helping with financial planning.2. RERA Registration is MandatoryBuilders must register under RERA (Real Estate Regulation and Development Act). This adds a layer of transparency and legal protection for the buyer.3. Scope for CustomisationBuyers may request minor changes in layout, flooring, or fittings during the construction phase.Legal Disadvantages of Under-Construction Properties1. Possession Delay RiskDespite RERA, delays of 1–2 years are still common, especially in West Bengal where monitoring is lax.2. Developer Fraud or AbandonmentNumerous cases in New Town and Salt Lake Extension areas involve builders collecting funds but failing to deliver.📌 Example: A 2022 Calcutta High Court case involved a Rajarhat builder promising possession within 24 months but defaulting for over 5 years. Buyers had to litigate for refund and interest.3. Hidden Encumbrances on LandBuilders may start projects on land that is disputed, mortgaged, or under acquisition. Without legal due diligence, the buyer’s money is at risk.4. GST Applies5% GST is applicable (without Input Tax Credit) for under-construction flats, adding to the total cost.What Legal Due Diligence Must Be Done—For Both TypesWhether buying ready or under-construction property, the following legal checks are essential:For Ready-to-Move FlatsTitle search report (at least last 30 years)Occupancy Certificate (OC)Completion Certificate (CC)Mutation & Property Tax clearanceChain of documents (including Sale Deed, Conveyance, etc.)Verification of No Dues from Society or BuilderEncumbrance CertificateFor Under-Construction FlatsRERA Registration Number & StatusSanctioned Building PlanCommencement CertificateLand Title Report (verify if land is freehold, residential, and owned by builder)Development Agreement and Power of Attorney of builderAgreement for Sale vetted by legal expertsHow Our Law Firm Can HelpAt KHA ADVOCATES, we’ve assisted hundreds of NRI and first-time buyers in verifying and registering properties across Kolkata. Our services include:1. Property Title VerificationGet a comprehensive title search report with legal opinion—ensuring you don’t invest in disputed or encumbered flats.2. Agreement Drafting & ReviewWe vet or draft Agreement for Sale, Sale Deed, or Builder-Buyer Agreement to protect your interests.3. RERA Compliance & Builder Due DiligenceWe check the track record, RERA filings, and legal standing of the builder and construction status.4. Property Registration SupportOur team handles property registration, stamp duty calculation, and sub-registrar office coordination on your behalf—even without your physical presence.Conclusion: Choose Wisely, LegallyThe choice between ready-to-move and under-construction properties must balance your budget, timeline, and risk appetite. But one thing is non-negotiable—legal due diligence.In Kolkata’s fast-growing property landscape, especially in New Town, Rajarhat, and Salt Lake, blind trust on builders can cost you lakhs. But with the right legal partner, you buy safely, confidently, and profitably.📞Need Legal Help Before Buying a Flat in Kolkata?👉 Book a consultation with our real estate legal experts👉 Call us at 94-777-5-888-5👉 WhatsApp us at 8101-555-666👉 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in👉 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com
Read More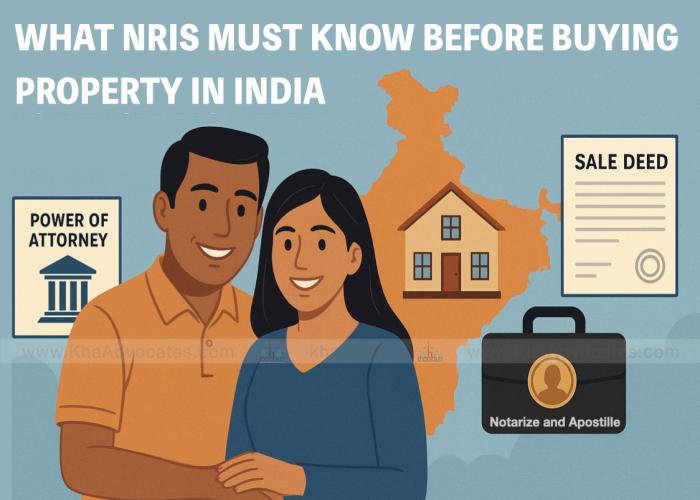
India has always been an attractive destination for Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) looking to invest in property—whether it’s a flat in the heart of Mumbai, a villa in Goa, or a retirement home in their hometown. With a booming real estate market and emotional ties to the homeland, it’s no surprise that thousands of NRIs buy properties in India every year.But here’s the catch: buying property in India as an NRI involves legal complexities that must be carefully handled to avoid risks like title disputes, fraud, or procedural delays. The good news? With the right legal team and planning, you can invest in Indian real estate without even flying down.This guide walks you through everything NRIs must know before buying property in India—especially about Power of Attorney, Sale Deed registration remotely, and how to ensure a safe and legally compliant transaction.Who Can Buy Property in India as an NRI?As per FEMA (Foreign Exchange Management Act) regulations, NRIs and PIOs (Persons of Indian Origin) can buy:Residential properties (flats, houses, plots)Commercial propertiesHowever, agricultural land, plantation property, or farmhouses cannot be purchased by NRIs without special permission from the RBI.Must-Have Documents Before You ProceedTo start the process, make sure you have the following ready:Indian Passport or OCI CardPAN Card (mandatory for property transactions)Address Proof (local and overseas)Recent photographsNRE/NRO Bank Account for financial transactionsPower of Attorney (if you cannot travel to India)Power of Attorney (PoA): Your Legal Key When You’re AbroadIf you are not physically present in India to oversee the purchase, the Power of Attorney (PoA) is your best legal solution. It allows a trusted person—usually a relative, friend, or lawyer—to act on your behalf.Types of PoA You Can Use:General Power of Attorney: Broad powers for managing or selling property.Special Power of Attorney: Limited to specific acts like signing a sale deed, submitting documents, etc.How to Execute a PoA from Abroad:Draft the PoA: Work with an Indian legal expert to draft a PoA customized to your transaction.Notarize and Apostille it in your country of residence (as per Hague Convention rules).Send it to India via post or courier.Adjudicate the PoA at the local Sub-Registrar Office in India within 90 days of receipt.Legal Tip: Always specify exact powers and property details to prevent misuse.Can NRIs Register Property in India Without Visiting?Yes. NRIs can register the Sale Deed remotely through their attorney holder, provided the PoA includes registration rights.Here’s how it works:Execute a registered Sale Agreement.PoA-holder attends the Sub-Registrar Office for Sale Deed registration.All payments (including stamp duty and registration charges) are made from the NRI’s NRE/NRO account.This process ensures complete compliance while saving you travel expenses and time.Legal Checks Before You BuyTitle VerificationEnsure the property title is clear, marketable, and free from encumbrances. Your legal team should:Verify ownership documentsCheck the mutation recordsReview past Sale DeedsConduct searches in the Registrar’s OfficeBuilder or Seller Due DiligenceIf you’re buying from a developer, check:RERA registrationLand ownership documentsApprovals from local authoritiesFor resale properties:Identity and ownership of the sellerEncumbrance Certificate for last 30 yearsDues (property tax, society dues, utility bills)Stamp Duty & Tax ComplianceNRIs must pay applicable stamp duty and registration charges, and ensure:TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) is deducted as per Indian Income Tax ActPAN is linked and updatedCapital Gains implications are understoodWe assist NRIs in full tax compliance and documentation from start to finish.Online Property Services Now Available for NRIsIndian states like Maharashtra, West Bengal, Karnataka, and Delhi have digitized large parts of the property registration and land records system.Services you can access online:Property title searchSale Agreement draftingPoA processingOnline submission of documentsMutation applicationWith the right law firm, everything from property search to final registration can be done virtually.Real Case Example: How KHA ADVOCATES Helped an NRI Buy a Flat in Kolkata Without Visiting Indiafew of our NRI client from the UK, US, Australia wanted to purchase a resale flats in New Town, Rajarhat, Salt Lake, Kolkata. they executed a Special Power of Attorney, got it apostilled, and sent it to us. We verified the title, negotiated with the seller, executed the Sale Agreement, paid stamp duty, and registered the deed—all within 45 days.He didn’t have to step foot in India—and yet, the entire transaction was legally compliant and fully secure.Want to Buy Property in India Without Hassles?At KHA ADVOCATES, we specialize in end-to-end property legal services for NRIs, including:Power of Attorney drafting and adjudicationProperty title search & verificationSale Deed preparation & registrationMutation and name transferProperty tax and legal due diligenceWhether you’re buying a new home, resale property, or investing in a commercial space, our NRI Property Legal Team ensures a smooth and legally secure transaction—without you having to travel to India.📞 Let’s TalkIf you’re an NRI planning to buy property in India, don’t take chances. Talk to our legal experts, Book Consultation today.✅ Call Now: +91-94777-58885🌐 Visit: www.khaadvocates.com📧 Email: contact@khaadvocates.inSecure Your Dream Property in India—Without the Stress.Partner with the experts in NRI Property Law.This article is published by KHA ADVOCATES—India’s leading NRI Property Legal Advisors.
Read More
Buying property in Kolkata’s booming New Town or Salt Lake? Don’t rely on glossy brochures or verbal promises alone. Always get a professional Title Search (Property Search) Report to uncover the truth. This legal due-diligence document traces a property’s ownership history, encumbrances, municipal records and approvals . It confirms that the seller has a marketable title – meaning no hidden mortgages, disputes or illegalities. As one expert explains, a title search “ensures the seller has the legal right to sell the property and that there are no hidden issues” . In contrast, many buyers have been blindsided by attractive brochures that promise the moon. The remedy is simple: trust the search report, not just the builder’s words.High-rise apartments in Kolkata’s New Town – always verify the title behind the glossy façade. A comprehensive property search report reveals the true ownership, encumbrances (like loans or legal claims), and municipal approvals for a property .What Is a Property Title Search Report?A Title Search Report (often called an Abstract of Title) is a detailed dossier on a property’s legal history. It includes a chain of title (all previous owners), copies of sale deeds and other conveyance instruments, and a summary of any liens or encumbrances (mortgages, tax dues, lawsuits, etc.) . Lawyers prepare it by examining records at the sub-registrar’s office, revenue department and municipal corporation. They verify each transfer of ownership (sale deeds, gift deeds, wills, etc.) to ensure the vendor truly owns the land and has followed all legal formalities . By law, every sale of immovable property must be by a registered deed , so title searchers pull decades of registry records (often 30+ years back) to check the entire chain of transfers . The finished report spells out exactly who owns the land, the legal description (location and area), and any burdens on the title .In short, the title search report tells you “Is this property really safe to buy?” It answers questions like: Does the seller have absolute ownership? Were all past transfers registered correctly? Is there any pending mortgage, tax lien or court case on record? Answers come from official documents: registered sale deeds, Encumbrance Certificates, mutation records, approved plans, and more . These facts can’t be faked: “by doing title verification you can scrutinize that the transferor is the real owner of the property and has the power to transfer it” . In practice, you hire a property lawyer (often called a title search lawyer in Kolkata) to prepare this report. They physically inspect original title deeds and obtain certificates (like non-encumbrance certificates) from the government offices. The result is a written legal opinion confirming whether the title is clear and marketable .Why Is Title Verification Crucial?Real estate is a huge investment – and anywhere, unscrupulous sellers or builders may try to sell what they don’t fully own. Indian courts emphasize a basic rule: “a vendor cannot confer a better title upon the vendee than he himself possesses” . In other words, if the builder or seller doesn’t have clear title, neither will you. A thorough title search report prevents you from unknowingly buying disputed land. For example, if the property has an unpaid bank mortgage, you could become liable for that debt after purchase. The title report would flag any such encumbrances on the land .Key benefits of the search include:Confirming Clear Ownership: It ensures that the seller truly owns the property free of claims . A registered sale deed is “conclusive proof of ownership” under law , so the lawyer checks all past sale deeds. If any link in the chain is missing or forged, the report uncovers it.Identifying Mortgages & Liens: The report lists any registered mortgages or legal charges (like bank loans) on the title . You cannot know about hidden loans without this search.Uncovering Litigation: It reveals if the property has been involved in court cases or tax recovery proceedings . A prior lawsuit over boundaries or ownership should be known before you buy.Ensuring Conversion and Compliance: In Kolkata, agricultural land often needs a conversion certificate (per West Bengal Land Reforms Act) before it can be sold as residential or commercial. A search report verifies such certificates (or lack thereof) with revenue authorities. It also checks if municipal plans and building approvals are in order .Adhering to RERA & Registration Requirements: If the project is subject to RERA (2016), the promoter must submit legal title deeds and an Encumbrance Certificate when registering . Buyers can verify these RERA disclosures. Likewise, the Sale Deed you sign must be registered (as per the Registration Act) to be valid , and the title search ensures all past deeds were registered properly.In short, a property search report lets you negotiate from a position of knowledge. If the report shows a clean title, you proceed with confidence; if it shows issues, you can demand fixes, price adjustments, or simply walk away. It is your safest guard against ugly surprises.Real-Life Cautionary Tales from KolkataEven in reputed markets like Kolkata, builders have cut corners or over-promised. Real buyers have lost big by skipping due diligence. For instance, in New Town’s Teen Kanya housing project, over 400 buyers invested in a Bengal Shelter Housing Development scheme because a state housing board had a 49% stake . But the project stalled and was eventually taken over by SBI to recover dues. The flats remain half-finished, and the buyers are fighting to recover their money . If those home-buyers had insisted on a thorough title and loan history check, they might have spotted the developer’s financial troubles early.In Salt Lake, a realtor was caught forging a deed in a notorious fraud. He took ownership of a plot belonging to a man who had died 25 years ago by simply faking the owner’s signature . A relative only discovered the scam when she saw a new building on the old homestead. It turned out the fraudster had submitted forged documents to the registrar of assurances and “sold” the plot without any legitimate right . A proper title search (including checking death records and mutation entries) would have exposed this forgery.Another example: a “former naval officer” in Salt Lake ran a land fraud ring by showing buyers fake documents inflating land prices . He used phony registers of title to cheat one victim of ₹40 lakh. Police noted he preyed on buyers’ ignorance by fabricating better-than-market rates . Title search would have caught the discrepancy between the actual revenue records and the inflated figures he showed.These cases illustrate a common theme: buyers who rely on the builder’s word alone get cheated. Court decisions underscore that promotions are not always binding . For example, a Bombay High Court case held builders must honor brochure promises , but the safest path is not to take chances. Never sign anything until a lawyer confirms the title is clean. As one guide warns, “You cannot just rely on information provided in the sales brochure or on oral information by the seller” .Applicable Laws Every Buyer Should KnowWhen buying property in West Bengal, several laws are at play:Transfer of Property Act, 1882: Defines how immovable property is sold or gifted. Section 54 says a sale of immovable property (over ₹100) must be made by a registered instrument. Thus every sale deed should be registered with the Sub-Registrar . The Act also codifies the principle that a seller cannot give a better title than he has .Registration Act, 1908: Reinforces that sale deeds and similar conveyances be registered. A registered deed is considered “conclusive proof” of ownership unless shown otherwise . The title search report literally relies on scanning decades of such registered deeds.West Bengal Land Reforms Act, 1955: Regulates land ceilings and conversion. Under this, agricultural land often needs official conversion to be sold for non-agricultural use. The lawyer must verify that appropriate land conversion certificates are on record – otherwise the sale could be deemed illegal.RERA (2016): The Real Estate (Regulation & Development) Act requires most residential/commercial projects to register with the state RERA authority. Promoters are required to submit legal title deeds of the land and an Encumbrance Certificate when registering the project . RERA’s purpose is to protect buyers from project delays and misrepresentation, so buying only in a RERA-registered project is safer. Under RERA rules, promoters must also update buyers on approved plans and permit certificates .Local Laws and NOCs: In Kolkata, local authorities like HIDCO/NKDA (for New Town) or BMC (for Salt Lake) must approve building plans. A title search includes checking municipal records for sanction plans, occupancy certificates, and that property taxes are fully paid . Failure to check these could leave you with an illegal building.By citing these laws, a good lawyer ensures every document – from title deeds to building approvals – is examined. For example, our title search would verify compliance with RERA and check that all requisite NOCs (e.g. from NKDA for New Town plots) are obtained. The goal is to leave no stone unturned in proving the title is marketable and legally transferrable .What a Search Report ContainsA typical Property Search Report prepared by a lawyer will include (at minimum):Property Details: Exact location, dimensions, and Khatian/khasra numbers of the land .Ownership History: Identification of each owner (individual, company or trust) over the search period, with copies of title deeds (sale deeds, gift deeds, wills, etc.) that transferred ownership . A clear table of all verified documents is usually attached .Right of Transferor: Confirmation whether the current seller has absolute title or only a restricted right (for example, sometimes only a long lease or limited rights) .Encumbrances: Listing of any charges, mortgages or liens (bank loans, maintenance dues, etc.) on the property . This includes checking for unpaid municipal taxes or other statutory dues with the city corporation .Easements and Third-Party Interests: Disclosure of any easements (like rights of way) or third-party claims on the land .Litigation/Aquisition: Whether the property is embroiled in any pending court case, or is under government acquisition proceedings .Regulatory Compliance: Statement on whether the land is correctly classified (agricultural vs non-agricultural) , and if all municipal building approvals (plan sanctions, occupancy certificate) are in order .Final Opinion: A clear conclusion on whether the title is “clear and marketable”, along with any special remarks (for example, recommending specific precautions or highlighting minor defects) .Each item above is backed by local records (e.g. the sub-registrar’s index, Mutation Register, Court documents). For instance, the lawyer will obtain an up-to-date Encumbrance Certificate from the Sub-Registrar to ensure no unregistered transactions. They will also check mutation entries in municipal or land records to confirm the seller’s name appears properly . Remember, though mutation records show the revenue acknowledgement of transfer, they are not conclusive proof of title on their own . That’s why registered deeds are the primary evidence.Signing a sale deed only after legal due diligence: our title search lawyers review every document on your behalf. A professional report arms you with facts, not promises . It is prepared by a qualified lawyer – one who personally visits the local registrar’s office, inspects the original deeds, and collates certificates (like non-encumbrance and tax-clearance certificates). This thorough process cannot be rushed, but it pays off by shielding you from fraud or legal troubles down the road .How KHA Advocates Can HelpAt KHA ADVOCATES, our Kolkata-based property lawyers specialize in end-to-end legal services for homebuyers and investors. If you’re considering a purchase in New Town, Salt Lake or anywhere in Kolkata, we provide:Title Verification & Property Due Diligence: We conduct the full search and report as above, covering title deeds, encumbrances, land use, sanctioned plans, and more.Drafting and Reviewing Agreements: Our team drafts or reviews the Agreement for Sale to ensure all negotiated terms (price, area, amenities, timelines) are correctly captured in writing.Sale Deed Drafting & Registration: We prepare the Sale Deed for execution, assist with stamp duty calculations, and oversee the registration process at the sub-registrar’s office.Municipal and Utility Clearances: We help secure occupancy certificates, water/electricity connections, and ensure all local dues are cleared in the buyer’s name.NRI Property Legal Services: For Non-Resident Indians investing in Kolkata real estate, we offer full representation via Power of Attorney. NRIs are particularly vulnerable to title risks since they are away from India . Our lawyers can complete all title checks and document formalities on your behalf, saving you time and safeguarding your interests.RERA Compliance: We verify that your project is RERA-registered and that the promoter has submitted required documents (like title deeds and EC) to the authority .Our clients benefit from our local expertise. For example, we know that New Town plots fall under HIDCO/NKDA jurisdiction, so we confirm all required NOCs from these bodies. In Salt Lake, we ensure the land account (alekh) is updated in your name. With our assistance, you avoid pitfalls like missing mutation records or unnotified construction changes.Key Takeaway: Even a small oversight can cause big losses. Don’t skimp on legal help. The few hours and fees spent on a proper title search and lawyer’s review can save you lakhs or even crores later. As one guide notes, title verification can “alleviate the risk involved in the transaction” and save you millions .Steps to Protect Your InvestmentInsist on a Lawyer: From day one, involve a reputed title search lawyer in Kolkata (like KHA Advocates) rather than relying on broker or builder alone.Obtain Original Title Documents: Have the seller provide original sale deeds back as far as possible (ideally 30 years). Our attorney will check these against registry copies .Verify Encumbrance Certificate: Ask for the latest Encumbrance Certificate from the local sub-registrar (covering the last 13+ years). We will examine it for any unsurfaced liens or pending mortgages .Check Mutation & Tax Records: Ensure the property taxes and utility bills (land, water, electricity) are paid and that the mutation is duly recorded in the current owner’s name . Our team will collect up-to-date receipts and mutation certificates.Confirm Land Use: If the land was agricultural, make sure a conversion certificate is on file. For any property in Kolkata, confirm the land is correctly zoned (residential/commercial) with the authorities .Review Approvals: Verify that building plans, permits and occupancy certificates have been obtained from municipal authorities and conform to sanctioned plans . We cross-check RERA disclosures and city approvals.Document Everything: Ensure all promises (like gym, garden, parking) are written into the Agreement. Do not rely on brochures. If the developer made a representation, demand it be committed to writing and registered in the deed .By following these steps, you use your legal rights and avoid blind spots. Remember that money paid or flats booked under vague terms can vanish. It’s far safer to pay a lawyer than to pay a fraudster’s fine in court.ConclusionA Builder May Lie, the Search Report Doesn’t. The property title search report is your most reliable shield against fraud and hidden defects. It brings clarity, confidence and legal certainty to your purchase. Especially in markets like New Town and Salt Lake, where development is rapid, doing due diligence is non-negotiable.Protect yourself with KHA ADVOCATES’ expert legal team. We offer comprehensive title verification and property due diligence in Kolkata so you can buy with peace of mind. Book a consultation today or download our Free Property Due Diligence Checklist to get started.Don’t gamble with your dream home or investment. Schedule a meeting now and let us safeguard your interests.
Read More
Buying a flat in Kolkata is a significant milestone—especially for first-time home buyers and NRIs looking to invest in India. With Kolkata’s real estate market expanding across locations like Rajarhat, New Town, Salt Lake, Garia, and Behala, it’s easy to get overwhelmed by the options.However, this excitement often leads to rushed decisions—and costly mistakes.At KHA ADVOCATES, we’ve helped hundreds of property buyers avoid legal traps, save lakhs in taxes, and secure their dream homes with confidence. Here’s our expert guide on the 8 most common mistakes to avoid before buying a flat in Kolkata.1. Skipping Legal Title VerificationWhy it’s a mistake:Many buyers trust the builder’s brochure or online listing without verifying the legal title of the property. Flats built on disputed, encroached, or unauthorized land can lead to years of litigation.What to do instead:Hire a qualified property lawyer in Kolkata to conduct a title search for 30+ years and verify ownership, encumbrance, mutation, and land conversion records.✅ Tip: Always ask for a lawyer-certified Title Verification Report before paying the booking amount.2. Ignoring Developer’s Credentials & Project ApprovalsWhy it’s a mistake:Even big-name builders can default. Many flats in Kolkata are sold without municipal plan sanctions, completion certificates, or RERA registration—making them legally weak.What to do instead:Ask for:Building Sanction PlanRERA Registration NumberFire & Environmental ClearancesPast Project Completion Records✅ Tip: Cross-check the developer’s RERA profile on West Bengal RERA portal.3. Not Executing a Proper Agreement for SaleWhy it’s a mistake:Verbal assurances or token money receipts are not enough. Without a registered Agreement for Sale, your rights as a buyer are legally unsecured.What to do instead:Your sale agreement must be:Drafted by your lawyer (not the builder’s)Include clauses for possession date, penalties, refund, force majeure, and exit optionsProperly stamped and registered under the Registration Act✅ Tip: Ensure all payments are linked to construction milestones, not fixed dates.4. Overlooking Property Tax, Mutation, and Utility DuesWhy it’s a mistake:Unpaid taxes and utility bills from the previous owner or builder become your liability after purchase. This also impacts future mutation or resale.What to do instead:Insist on:Property Tax Clearance Certificate (KMC/KMDA/Municipality)Electricity and Water Bill ReceiptsMutation Records from BLRO or Municipal Body✅ Tip: Ask your lawyer to conduct a due diligence report on all municipal records.5. Buying Without Checking Land Conversion & Zoning PermissionsWhy it’s a mistake:Flats built on agricultural or ceiling-surplus land are illegal and may face demolition or cancellation by government authorities.What to do instead:Your lawyer must verify:Conversion Certificate (from agricultural to residential use)Zoning Compliance under the Master PlanLand Category under the West Bengal Land Reforms Act✅ Tip: Avoid flats built on thika land, vested land, or tenanted land unless fully regularized.6. Trusting Brokers Without Legal OversightWhy it’s a mistake:Real estate agents may push for a fast deal without revealing hidden issues. Many are not legally trained to detect property frauds or incomplete approvals.What to do instead:Use brokers only for site visits or negotiations. For documentation and verification, always consult a qualified real estate lawyer.✅ Tip: KHA ADVOCATES can appoint a verified broker and negotiate directly on your behalf.7. Failing to Register the Flat ProperlyWhy it’s a mistake:Even after full payment, if the Sale Deed is not registered, you are not the legal owner. Unregistered flats can’t be mortgaged, sold, or inherited.What to do instead:Ensure that:Sale Deed is drafted by your lawyerCorrect stamp duty is calculated (with NRI/TDS considerations if applicable)Registration is done before the Sub-Registrar✅ Tip: We assist NRIs with online registration appointments, digital POA execution, and sub-registrar compliance.8. Ignoring Tax Implications and Home Loan ClausesWhy it’s a mistake:Tax defaults, wrong home loan structuring, or not availing deductions under Section 80C/24B can cost you lakhs in lost benefits or future penalties.What to do instead:Get tax planning advice for:Capital gains (if selling old property)TDS on NRI transactionsJoint ownership and HUF benefitsLoan EMI deductions✅ Tip: Ask KHA ADVOCATES for a full tax advisory before loan sanction or final registration.Conclusion: Buy Smart, Buy LegalKolkata’s flat market is booming—but smart buyers invest with legal protection.Whether you’re an NRI investing from abroad, a young couple buying your first home, or a senior citizen securing retirement property, avoiding these 8 mistakes will save you from years of legal and financial trouble.Why Choose KHA ADVOCATES?At KHA ADVOCATES, we specialize in:✅ Property Title Verification✅ Agreement & Sale Deed Drafting✅ NRI Power of Attorney & Property Registration✅ Legal Due Diligence Reports✅ Tax Planning & Home Loan Support✅ Flat Mutation & Municipal Compliance👇 Need Legal Help Before Buying a Flat in Kolkata?📞 Call us now at +91-94-777-5-888-5💬 WhatsApp: 8101-555-666📩 Email: contact@khaadvocates.in🌐 www.khaadvocates.com🔒 Book a Free 15-Minute Consultation With a Property LawyerFAQs:Q1. I live abroad. Can I buy a flat in Kolkata without coming to India?Yes, we help NRIs with Power of Attorney, digital due diligence, and end-to-end legal support.Q2. Can I verify the flat’s title before booking?Absolutely. Our Title Search Services verify 30+ years of ownership and municipal records.Q3. How much stamp duty will I pay while registering the flat?It depends on the flat value and location (KMC, Rajarhat, Howrah). Contact us for a precise calculator.
Read More
In a major digital governance initiative, the Department of Urban Development & Municipal Affairs, Government of West Bengal, has launched E-Mutation services via its online portal https://wburbanservices.org. This facility enables property owners within Bidhannagar Municipal Corporation (BMC) to apply for mutation of property records from the comfort of their home—without visiting municipal offices.This article explores the mutation process, the benefits of the E-Mutation portal, and how KHA Advocates, a premier legal service provider for property matters in West Bengal, can assist you throughout the procedure.🔍 What Is Property Mutation?Mutation refers to the process of changing the title ownership of a property in government records after it is transferred via sale, gift, inheritance, or will. It is essential for updating tax liabilities and establishing legal ownership in civic records maintained by the municipal body.🌐 About the WB Urban Services E-Mutation PortalThe wburbanservices.org portal is a centralized platform that enables digital mutation applications for urban areas. The Bidhannagar region is among the first to benefit from this online initiative.✅ Key Features:Online application submissionUpload of property documents in PDF formatStatus tracking of applicationSMS/Email alertsOnline approval and certificate download🏙️ Who Can Apply Through This Portal?Anyone who owns property within the Bidhannagar Municipal Corporation (BMC) limits—covering areas like Salt Lake, Rajarhat, and parts of New Town—can apply for:Mutation due to sale deedMutation due to inheritance/successionMutation after partition or giftMutation upon registration of leasehold to freehold conversion📝 Documents Required for E-MutationRegistered Sale/Gift/Partition/Will DeedCopy of current tax billPrevious mutation certificate, if anyAadhar Card or Voter ID of the ownerAffidavit (if applicable)Succession certificate (for inheritance cases)🔄 Step-by-Step Process for E-Mutation on the PortalVisit https://wburbanservices.orgRegister/Login using your mobile number or emailSelect Municipality: Choose Bidhannagar Municipal CorporationFill Application Form: Enter property details, deed reference, applicant infoUpload Documents: Attach scanned copies (PDF only)Pay Online Fee (if applicable)Submit ApplicationTrack Status and download certificate once approved⚖️ How KHA Advocates Can Help YouAt KHA Advocates, we understand that even digital processes can be complex for first-time users or NRIs. Our expert team offers end-to-end assistance in:Title verification before mutationDrafting and notarizing mutation affidavitsEnsuring correct document format for uploadFiling applications on your behalfLegal support for disputed ownership or rejectionAssistance in mutation for inherited and leasehold propertiesWe provide mutation services for both NRIs and local clients, ensuring compliance, accuracy, and timely execution.📌 Why Choose KHA Advocates for E-Mutation?Dedicated Mutation ExpertsExperienced with Bidhannagar Property LawsFast-track Processing for NRIsOn-ground Support in Salt Lake & RajarhatReal-time Application Monitoring
Read More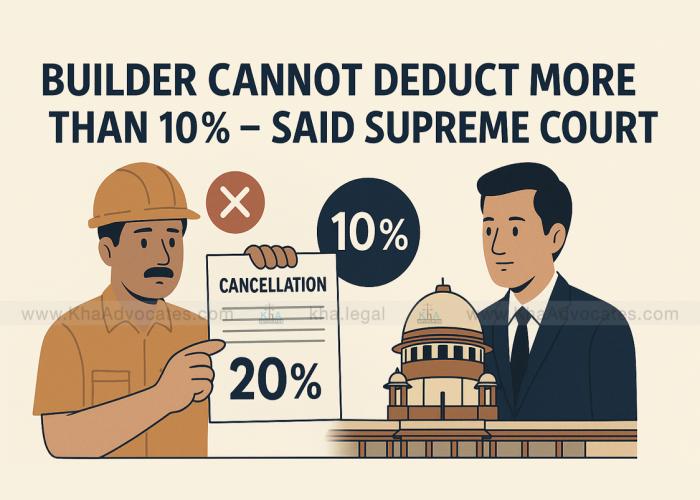
🏗️ IntroductionIn a landmark decision that strengthens consumer rights, the Supreme Court of India has ruled that builders cannot deduct more than 10% of the total flat cost when a buyer cancels the booking. The judgment comes as a relief to countless homebuyers who have faced unfair deductions from real estate developers during cancellations. This ruling sets a powerful precedent and aligns with the principles of fairness and reasonableness under Indian contract and consumer protection law.Background: Why This Issue MattersOver the years, many homebuyers have reported instances where real estate developers deducted 20%, 25%, or even 30% of the total property value when a buyer decided to cancel the booking, often without starting construction or incurring any loss.This unfair trade practice prompted legal intervention, and the judiciary has now taken a stand to protect buyers from arbitrary contract clauses that are heavily biased in favour of builders.Supreme Court Ruling: Key HighlightsIn the case of Wg. Cdr. Arifur Rahman Khan & Ors. v. DLF Southern Homes Pvt. Ltd., the Supreme Court upheld the consumer-friendly interpretation that if the builder has not incurred a substantial loss or started construction, they cannot deduct more than 10% of the booking amount or flat price.Important Takeaways:Maximum Deduction Limit: Builders can deduct no more than 10% in case of cancellation.Beyond 10% is arbitrary and amounts to unjust enrichment.Unilateral terms in builder-buyer agreements that allow excessive deductions are unconscionable and voidable.The builder cannot use delay tactics or unjust contract terms to deny fair refunds.⚖️ Legal Reasoning: Supreme Court’s AnalysisThe Court based its ruling on several legal principles:Principle of Unconscionable ContractsWhen one party (the builder) has excessive bargaining power, the Court can strike down oppressive terms.Citing Central Inland Water Transport Corporation v. Brojo Nath, the Court emphasized that contractual terms must be reasonable and fair.Consumer Protection ActThe Court reaffirmed that a buyer is a consumer and entitled to just treatment under Sections 2(1)(d) & 2(1)(r) of the Consumer Protection Act.Builders indulging in excessive deduction are guilty of unfair trade practices.Doctrine of ReasonablenessBuilders are not permitted to make windfall gains from cancellations.Refund policy must reflect actual losses, not speculative penalties.Other Important Judgments on the SubjectKailash Nath Associates v. DDA [(2015) 4 SCC 136]The Court held that forfeiture of earnest money is only valid if the party has suffered a loss. Builders must prove actual damage for withholding more than 10%.Haryana Urban Development Authority v. Dropadi DeviOnly reasonable forfeiture is allowed. Excessive deduction without justification is illegal.RERA Provisions – Section 18 of RERA Act, 2016The buyer is entitled to full refund with interest if the builder fails to deliver on time. Deductions exceeding 10% are in direct conflict with RERA’s spirit.What It Means for HomebuyersIf you have cancelled your flat booking and the builder is withholding more than 10%, you have a strong legal remedy. The following steps are advised:📋 What You Can Do:Send a legal notice seeking full refund minus 10%.File a complaint with the Real Estate Regulatory Authority (RERA).Approach Consumer Court if builder refuses or delays refund.Maintain booking receipts, payment records, and correspondence as evidence.Precautionary Measures for Future BuyersRead the Builder-Buyer Agreement thoroughly before signing.Negotiate clauses related to cancellation and refund.Prefer builders registered under RERA with transparent refund policies.Get legal vetting of the agreement from a property lawyer.How KHA Advocates Can HelpAt KHA Advocates, we assist homebuyers in fighting against builder malpractices, securing rightful refunds, and filing RERA and consumer complaints. Our team of real estate and litigation experts ensures your legal rights are protected.📞 Book a Consultation: https://khaadvocates.com/book-consultation🏢 Representing clients in Supreme Court, High Courts, RERA & Consumer ForumsConclusionThe Supreme Court’s ruling offers much-needed relief and clarity to homebuyers. By capping the builder’s deduction at 10%, the Court has reaffirmed the principle that contracts cannot override fairness and public interest. Homebuyers must remain informed, vigilant, and assertive in asserting their rights.
Read More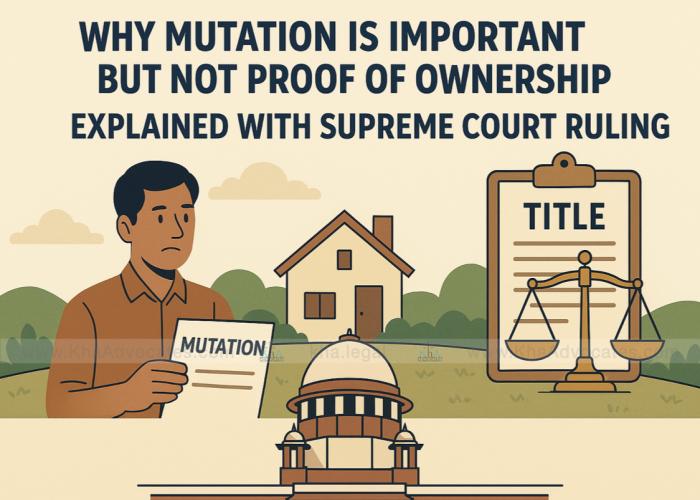
IntroductionMany landowners and property buyers in India mistakenly believe that mutation of property is equal to legal ownership. However, as clarified by the Supreme Court of India and several High Courts, mutation is merely a fiscal or administrative process and does not confer any title. This blog decodes the importance of mutation, its legal status, and critically examines landmark Supreme Court judgments that definitively settled the issue.What Is Mutation of Property?Mutation refers to the process of updating land or property records in the revenue department once ownership is transferred through sale, inheritance, gift, or will. It enables the government to assess and collect property tax from the rightful person.In simple terms, mutation reflects who is in possession for tax purposes, but it is not conclusive proof of ownership.Why Mutation Is ImportantWhile mutation is not ownership, it is still crucial for several reasons:It helps the government maintain updated land records.It ensures that the property tax is paid by the current possessor.It serves as a presumptive evidence of possession, aiding in administrative matters.It is often required when applying for electricity, water, or municipal services.It can be used in courts to support a claim, though not as standalone proof.Supreme Court’s Stand: Mutation Is Not Title🏛 Balwant Singh v. Daulat Singh (1997) 7 SCC 137In this case, the Supreme Court held:“Mutation in the revenue record does not create or extinguish title nor has it any presumptive value on title. It only enables the person in whose favour mutation is ordered to pay the land revenue.”This judgment laid the foundation for the doctrine that revenue records are fiscal and not legal proof of ownership.🏛 Narendra v. State of Uttar Pradesh (2017) 9 SCC 426Here, the Supreme Court clarified:“Entry in revenue records is not a document of title. It merely reflects possession. Title must be established independently through documents such as sale deed, gift deed, or court decree.”This means a person can be shown as a possessor in mutation records but still not be the rightful owner.🏛 Jitendra Singh v. State of Madhya Pradesh (2021) 2 SCC 612A more recent case where the Court reiterated:“The mutation of land in revenue records does not confer ownership title to the person. It only confirms possession for revenue purposes.”This case also emphasized that if a person’s title is challenged, they must prove it through registered documents and chain of title – not mere mutation.Mutation vs Title: Understanding the Legal DifferenceAspectMutationLegal Ownership (Title)NatureAdministrative / fiscalLegal / proprietaryPurposeTax assessment, record updationConfers full rights and interest in propertyDocument RequiredApplication to revenue authoritiesRegistered sale deed / gift / will / court decreeProof of Ownership?❌ No✅ YesCan be challenged?✅ Easily❌ Not easily if legally registeredUse in litigation?Limited supportPrimary evidenceHigh Court Rulings on Mutation Not Being Ownership🏛 Madras High Court – K. Muthulakshmi v. The Tahsildar (2015)Held that:“Mutation entries in revenue records are neither conclusive nor final. Ownership has to be proved through valid title documents.”🏛 Delhi High Court – Ashok Kumar v. Delhi Jal Board (2012)The Court ruled that:“A mutated name in municipal records cannot be relied on to establish legal title. Mutation cannot replace a registered title deed.”Common Misconceptions About Mutation“If my name is in mutation, I am the owner.”❌ Wrong. You are merely the recognized possessor for tax purposes.“Mutation replaces the need for registration.”❌ False. Only a registered deed establishes title.“Mutation protects me from legal disputes.”❌ Not entirely. Without a valid title, your claim can be challenged.When Mutation Becomes Relevant in CourtAlthough mutation is not ownership, it can support a claim of possession when:There is no contesting title, andIt is combined with other evidence like tax receipts, utility bills, or long possession.Still, courts always look for legal instruments to decide ownership.Conclusion: Mutation Is Not Ownership – Know the Legal TruthIn conclusion, mutation is important for taxation and record maintenance, but it does not grant or prove ownership. Indian courts – including the Supreme Court – have consistently held that title must be proven through registered legal documents, not revenue entries.If you’re purchasing or inheriting property, always ensure you have:A registered title deedA clear chain of titleEncumbrance certificate & title searchAnd legal assistance for documentation📞 Need Expert Legal Help?At KHA Advocates, we specialize in property law, title verification, mutation correction, and real estate litigation. Our experienced team can ensure your property rights are secure and legally valid.📩 Contact Us Today or visit www.KhaAdvocates.com for a consultation.
Read More
Does mutation of property mean you’re the legal owner? Think again.In the world of Indian real estate, “mutation” is a commonly misunderstood term. Many believe that once a property is mutated in their name, they automatically become the legal owner. However, the Supreme Court of India has clarified this misconception through several landmark judgments. Let’s unpack what mutation really means—and more importantly, what it doesn’t.What is Mutation of Property?Mutation refers to the process of updating or recording the transfer of title of a property in the revenue records of the local municipal authority. This allows the government to charge property tax from the rightful person.Mutation may be required:After the purchase of propertyUpon inheritanceVia gift deed or willThrough a court decreeHowever, mutation is not a document of title. It is merely a fiscal record maintained for administrative purposes.⚖️ Supreme Court’s View on Mutation & Ownership🏛️ Key Judgement: Balwant Singh vs Daulat Singh (1997) 7 SCC 137The Supreme Court held that mutation entries do not confer any title nor do they have any presumptive value on ownership. They are primarily for revenue collection and cannot be used as conclusive proof of ownership in a court of law.“Mutation does not create or extinguish title. It does not have any presumptive value on ownership.”– Supreme Court, Balwant Singh vs Daulat Singh🏛️ Municipal Corporation of Greater Bombay vs. Lala Pancham (1965 AIR 1008)This judgment reinforced that mutation is not a mode of transfer of ownership. The Court stated that unless there’s a valid legal transfer through sale, gift, or inheritance, mutation cannot determine ownership rights.⚖️ High Court Judgments Supporting the Principle🏛️ Karnataka High Court – Nanjundegowda vs. State of Karnataka (2011)The Court held that revenue entries (mutation) are not documents of title, and ownership can only be proved by valid documents such as registered sale deeds, gift deeds, or court decrees.🏛️ Delhi High Court – Jagjit Singh vs. Union of India (2013)The Court clarified that even if someone’s name is entered in municipal records via mutation, it cannot override the rights of a person holding a legally registered title deed.❌ Common Myths About MutationMythRealityMutation = Ownership❌ No, it’s not proof of ownershipMutation means title transfer❌ Only legal instruments like sale/gift deed do thatMutation protects you in court❌ Courts rely on title documents, not revenue entries🧾 Legal Documents That Actually Prove OwnershipRegistered Sale DeedGift Deed (with mutation as a follow-up)Probated WillPartition DeedCourt Decree of Title📝 Why Mutation Still MattersWhile mutation doesn’t prove ownership, it is still crucial for property tax liability, obtaining building permissions, and utility connections. It ensures that the municipal records are up to date and that the right person is billed.Key TakeawaysMutation is not proof of ownership.It is a record for taxation and revenue purposes only.Ownership must be proved through registered legal documents.Supreme Court and High Courts have consistently ruled on this matter.Always consult a property lawyer before assuming mutation equals title.📞 Need Legal Help With Property Title or Mutation?At KHA ADVOCATES, we specialize in property law, title verification, mutation assistance, and litigation support across India. Our team handles disputes related to ownership, mutation denial, and false claims, backed by a strong record in High Courts and the Supreme Court.👉 Contact Us Now for a consultation!
Read More
The legal distinction between a Gift/Settlement Deed and a Will plays a vital role in property transfer and succession planning under Indian law. The Supreme Court of India, in a series of landmark judgments, has clarified the core legal principles that separate these two instruments. Understanding the difference is crucial to avoid future disputes, especially concerning immovable property.Definitions Under Indian LawGift Deed / Settlement DeedA Gift Deed, governed by Section 122 of the Transfer of Property Act, 1882, is a voluntary transfer of property by one person (donor) to another (donee) without consideration, accepted by the donee during the lifetime of the donor. A Settlement Deed is a broader document often used to distribute property among family members for future stability.Key Features:Immediate and irrevocable transferRequires registration under Section 17 of the Registration Act, 1908Stamp duty applicable as per state lawEffective during the lifetime of the settlor/donorWillA Will, as per Section 2(h) of the Indian Succession Act, 1925, is a legal declaration of the testator’s intention with respect to their property, which comes into effect only after their death.Key Features:Revocable until the testator’s deathNo stamp duty requiredRegistration is optional but advisableTakes effect posthumouslySupreme Court’s Interpretation: Key Judgments🔹 Thulasamma v. Sesha Reddy (1977)The Court held that the intention of the parties is paramount. Even if a document is titled a “Settlement,” if it confers rights only after the death of the settlor, it operates as a Will.🔹 Radha Ammal v. Camillus AIR 2006 SC 1781The Supreme Court clarified that nomenclature is not conclusive. A document labeled as a settlement deed may actually be a Will if the transfer is postponed until the death of the person executing the deed.🔹 K.K. Mohammad Ali v. State of Kerala (2010) 1 SCC 417It was emphasized that the timing of when the rights vest in the beneficiary is critical. If vesting is immediate, it’s a gift/settlement. If it’s deferred till death, it’s a will.Key Legal Differences SummarizedAspectGift/Settlement DeedWillTakes EffectImmediatelyAfter DeathRevocabilityIrrevocableRevocableStamp DutyMandatoryNot RequiredRegistrationMandatoryOptionalConsiderationNot RequiredNot ApplicableVesting of RightsDuring Settlor’s LifetimeUpon Testator’s DeathWhy This Distinction MattersSuccession Disputes: Incorrect drafting may lead to family feuds and litigation.Tax Implications: Stamp duty and tax liability differ drastically.Validity Issues: Unregistered gift deeds may be invalid; unregistered wills may face challenge during probate.Pro Tips by KHA ADVOCATESUse Precise Language: Clearly express intention to avoid misinterpretation.Consult a Property Lawyer: Especially important for NRI clients dealing with Indian assets.Register All Deeds: Avoid ambiguity by registering gifts/settlements.Update Will Regularly: Changes in family or assets must be reflected promptly.ConclusionThe Supreme Court’s consistent stance makes one thing clear: intention and timing of vesting are the defining parameters. While both documents can be used to transfer property, choosing the correct one based on your situation is vital. Legal consultation ensures your assets are protected and your legacy preserved.
Read More
IntroductionSalt Lake City, officially known as Bidhannagar, was conceptualized and developed under the leadership of Dr. Bidhan Chandra Roy, the then Chief Minister of West Bengal. Conceived as a modern satellite township adjacent to Kolkata, the project involved the acquisition of wetlands and privately owned lands. These lands were subsequently allotted to individuals through lease agreements, each extending up to an unprecedented 999 years—ensuring government control while granting long-term occupancy rights.Initially, allotments were conducted through a lottery system. However, with time, the issue of property transfers within Salt Lake arose. The restrictive nature of lease deeds and the absence of a clear legal mechanism for transferring leasehold rights led many lessees to opt for unofficial means such as executing Powers of Attorney or Wills—resulting in a loss of revenue for the State.To address this issue and to establish legal clarity, the West Bengal government introduced a formal framework through a Gazette Notification in 2012. This article aims to provide a comprehensive and simplified explanation of the current legal position, procedures, and key judgments related to leasehold property transfers in Bidhannagar.Types of Lease Deeds in Salt LakeThe 17-Clause Lease DeedAmong the earliest lease agreements executed in the 1970s, the 17-Clause Lease Deed granted leaseholders more liberal terms, with no explicit restrictions on the transfer of property. Roughly 88 such deeds were issued to the first group of Salt Lake allottees.Due to the absence of any clause requiring government approval for transfer, leaseholders under this deed have historically enjoyed greater flexibility. Over the years, the Calcutta High Court has supported this interpretation, directing authorities to process mutations in favour of transferees without insisting on government permission.The 20-Clause Lease DeedUnlike the 17-Clause version, the 20-Clause Lease Deed contains specific restrictions that require prior approval from the Urban Development Department before any transfer of the leasehold property. These restrictive covenants are aimed at maintaining state oversight and regulating the sale of government-leased land.2012 Gazette Notification: Regulation of TransfersOn June 22, 2012, the West Bengal Government issued a Gazette Notification (No. 2709-SL(AL)/4S-9/2004(Pt-I)) introducing a formal transfer policy for leasehold plots in Bidhannagar. Key highlights include:Mandatory Government Approval: Transfer of leasehold rights requires prior permission from the Urban Development Department.Transfer Fee: A fee of ₹5,00,000 per cottah was introduced. However, exemptions apply for intra-family transfers (e.g., to parents or spouse).Regularization of Past Transfers: Past transactions conducted without government approval could be regularized upon payment of the transfer fee and completion of required formalities.Binding Lease Terms: All transfers are subject to the original lease terms, and the transferee inherits the obligations of the lease.This notification primarily targeted restrictive leasehold deeds (such as the 20-Clause Deed) but caused confusion regarding its applicability to 17-Clause Deeds.Landmark Judgment: State of West Bengal & Ors. vs. Ajay Poddar & Anr.This pivotal case resolved key ambiguities surrounding the 17-Clause Lease Deed. The issue before the Supreme Court was whether lessees holding 17-Clause Deeds could transfer their property without government approval or paying the transfer fee mandated in the 2012 notification.Supreme Court Ruling (March 11, 2015):The Apex Court ruled that the 17-Clause Deeds did not require government approval for transfers.The ₹5,00,000 per cottah transfer fee was deemed applicable only to restrictive lease deeds, such as those containing the 20 clauses.Past transfers executed without prior permission under 17-Clause Deeds were held valid, provided they complied with other legal requirements.Government agencies were directed to process mutations for such transfers without demanding approval or fees.This judgment provided significant relief to lessees and removed procedural bottlenecks for a large number of plot owners.2016 Circular: Simplification with ConditionsFollowing the Supreme Court judgment, the Urban Development Department issued Circular No. 693-UD/LM/SL(AL)-4S-5/2016 on May 4, 2016. This clarified the operational procedures for transferring 17-Clause Leasehold Plots:Prior Approval Not Required: Lessees need not seek permission from the government before transferring their plots.Mandatory Transfer Fee: Despite the removal of permission requirements, the transfer fee continues to apply—even for 17-Clause Deeds.Regularization of Past Transactions: Unauthorized transfers can be legalized upon payment of fees and proper documentation.This circular sought to balance ease of transactions with the state’s revenue interests and legal accountability.Step-by-Step Procedure to Buy Leasehold Plots in Salt Lake1. Document CollectionLease DeedAllotment LetterMutation Certificate (if applicable)Tax Clearance CertificateNo Objection Certificates (as applicable)2. Title Verification & Agreement PreparationConduct a thorough title search.Draft an “Agreement for Assignment of Lease” detailing sale price, terms, and responsibilities.3. Application for Transfer PermissionPrepare an application along with:Identity proof of buyer and sellerCertified copies of lease documentsAgreement for assignmentTax receipts and No Dues Certificate4. Online SubmissionRegister on the official portal of the Urban Development Authority.Upload notarized documents in PDF format (max 2MB each).Pay the application fee (currently ₹1,000).5. Verification ProcessAuthorities review documents and conduct physical inspection of the plot to match records.6. Hearing & Payment of Transfer FeeAttend the scheduled hearing with buyer, seller, and legal representatives.Pay the applicable transfer fee based on plot area.Submit draft deed for government approval.7. Deed RegistrationExecute and register the final Lease Transfer Deed at the designated registration office.The government issues a registration order upon approval.8. MutationSubmit the registered deed to the Urban Development Authority within 60 days.Apply for mutation to update ownership in official land records.Obtain a Mutation Certificate upon approval.ConclusionSalt Lake’s land transfer laws have evolved significantly since the township’s inception. The early liberal 17-Clause Lease Deeds offered flexibility, later reaffirmed by the Supreme Court, while the more regulated 20-Clause Deeds require strict compliance with transfer procedures.The 2012 notification and subsequent 2016 circular laid the groundwork for a structured and revenue-conscious framework. While these measures aimed to streamline transfers and reduce irregularities, practical challenges such as administrative delays and lack of public awareness continue to persist.Understanding the legal nuances and following proper procedures is crucial for any individual seeking to buy or transfer leasehold property in Bidhannagar. For smooth execution and legal compliance, it is strongly advised to consult experienced property lawyers familiar with Salt Lake’s unique lease framework.Need Legal Assistance for Salt Lake Property Transfers?At KHA ADVOCATES, our dedicated legal team provides expert assistance for lease deed reviews, mutation, registration, and title verification in Bidhannagar. Contact us today for a hassle-free consultation.📞 Call Now 94-777-5-888-5 | 🌐 Visit www.khaadvocates.comRelevant Links:Circular https://www.wburbanservices.gov.in/upload_file/circular/1721-ud.pdf2012 notification https://www.wburbanservices.gov.in/upload_file/file_doc/al_2709_3377.pdf88 Plots https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/city/kolkata/salt-lake-plot-transfer-begins-again/articleshow/53470533.cms
Read More
KhA Advocates is a premier law firm in Kolkata, West Bengal known Internationally, providing expert legal services in property registration, corporate law, matrimonial law, taxation, dispute resolution, and more. We offer tailored legal solutions for NRIs, businesses, and residents, ensuring 100% compliance and protection. With our efficient, transparent, and reliable approach, we safeguard your legal interests.
Copyright @2024 KHA Advocates
Designed by Webina Tech
Please read and accept our Terms & Conditions and Privacy Policy to continue using our site.